A composite robotic-based measure of upper limb proprioception
- PMID: 29132388
- PMCID: PMC5683446
- DOI: 10.1186/s12984-017-0329-8
A composite robotic-based measure of upper limb proprioception
Abstract
Background: Proprioception is the sense of the position and movement of our limbs, and is vital for executing coordinated movements. Proprioceptive disorders are common following stroke, but clinical tests for measuring impairments in proprioception are simple ordinal scales that are unreliable and relatively crude. We developed and validated specific kinematic parameters to quantify proprioception and compared two common metrics, Euclidean and Mahalanobis distances, to combine these parameters into an overall summary score of proprioception.
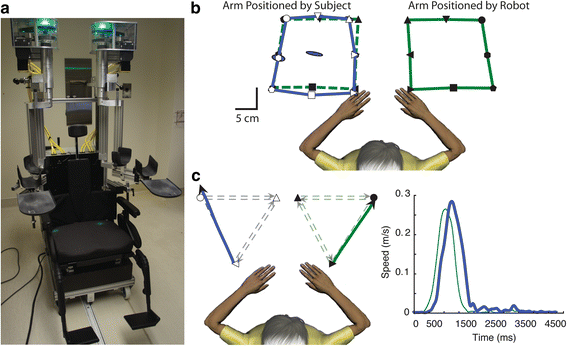
Methods: We used the KINARM robotic exoskeleton to assess proprioception of the upper limb in subjects with stroke (N = 285. Mean days post-stroke = 12 ± 15). Two aspects of proprioception (position sense and kinesthetic sense) were tested using two mirror-matching tasks without vision. The tasks produced 12 parameters to quantify position sense and eight to quantify kinesthesia. The Euclidean and Mahalanobis distances of the z-scores for these parameters were computed each for position sense, kinesthetic sense, and overall proprioceptive function (average score of position and kinesthetic sense).
Results: A high proportion of stroke subjects were impaired on position matching (57%), kinesthetic matching (65%), and overall proprioception (62%). Robotic tasks were significantly correlated with clinical measures of upper extremity proprioception, motor impairment, and overall functional independence. Composite scores derived from the Euclidean distance and Mahalanobis distance showed strong content validity as they were highly correlated (r = 0.97-0.99).
Conclusions: We have outlined a composite measure of upper extremity proprioception to provide a single continuous outcome measure of proprioceptive function for use in clinical trials of rehabilitation. Multiple aspects of proprioception including sense of position, direction, speed, and amplitude of movement were incorporated into this measure. Despite similarities in the scores obtained with these two distance metrics, the Mahalanobis distance was preferred.
Keywords: Kinesthesia; Outcome measure; Position sense; Proprioception; Robotics; Stroke; Upper extremity.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This research was approved by the University of Calgary Conjoint Health Research Ethics Board (#22123). All subjects provided written informed consent prior to study participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
Stephen H. Scott is cofounder and chief scientific officer of BKIN Technologies, the company that commercializes the KINARM robotic device used in this study. All other authors have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Fugl-Meyer AR, Jaasko L, Leyman I, Olsson S, Steglind S. The post-stroke hemiplegic patient. Scand J Rehab Med. 1975;7:13–31. - PubMed
-
- Brott T, Adams HP, Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG. Biller J, et al. A Clinical Examination Scale. Stroke: Measurements of Acute Cerebral Infarction; 1989. - PubMed
-
- Gowland C, Stratford P, Ward M, Moreland J, Torresin W, Van Hullenaar S, et al. Measuring physical impairment and disability with the Chedoke-McMaster stroke assessment. Stroke 1993;24:58–63. - PubMed
-
- Meyer S, Karttunen AH, Thijs V, Feys H, Verheyden G. How do somatosensory deficits in the arm and hand relate to upper limb impairment, activity, and participation problems after stroke? A Systematic Review Phys Ther. 2014;94:1220–1231. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

