Kinase profiling of liposarcomas using RNAi and drug screening assays identified druggable targets
- PMID: 29132397
- PMCID: PMC5683536
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-017-0540-x
Kinase profiling of liposarcomas using RNAi and drug screening assays identified druggable targets
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Kinase profiling of liposarcomas using RNAi and drug screening assays identified druggable targets.J Hematol Oncol. 2025 Nov 27;18(1):106. doi: 10.1186/s13045-025-01767-2. J Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 41310857 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Liposarcoma, the most common soft tissue tumor, is understudied cancer, and limited progress has been made in the treatment of metastatic disease. The Achilles heel of cancer often is their kinases that are excellent therapeutic targets. However, very limited knowledge exists of therapeutic critical kinase targets in liposarcoma that could be potentially used in disease management.
Methods: Large RNAi and small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor screens were performed against the proliferative capacity of liposarcoma cell lines of different subtypes. Each small molecule inhibitor was either FDA approved or in a clinical trial.
Results: Screening assays identified several previously unrecognized targets including PTK2 and KIT in liposarcoma. We also observed that ponatinib, multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, was the most effective drug with anti-growth effects against all cell lines. In vitro assays showed that ponatinib inhibited the clonogenic proliferation of liposarcoma, and this anti-growth effect was associated with apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase as well as a decrease in the KIT signaling pathway. In addition, ponatinib inhibited in vivo growth of liposarcoma in a xenograft model.
Conclusions: Two large-scale kinase screenings identified novel liposarcoma targets and a FDA-approved inhibitor, ponatinib with clear anti-liposarcoma activity highlighting its potential therapy for treatment of this deadly tumor.
Keywords: Kinase inhibitor; Liposarcoma; Ponatinib; Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
All animal experiments were performed according to the ethical regulations of Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the National University of Singapore.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors have declared a conflict of interest. Research support for JWT receive from Aptose, Array, AstraZeneca, Constellation, Genentech, Gilead, Incyte, Janssen, Seattle Genetics, Syros, Takeda, and the Scientific Advisory Board for Leap Oncology.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
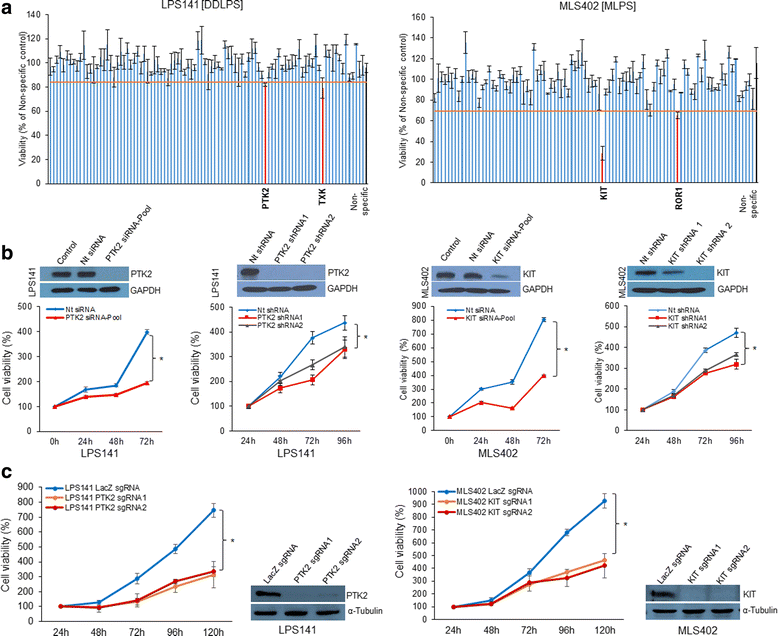
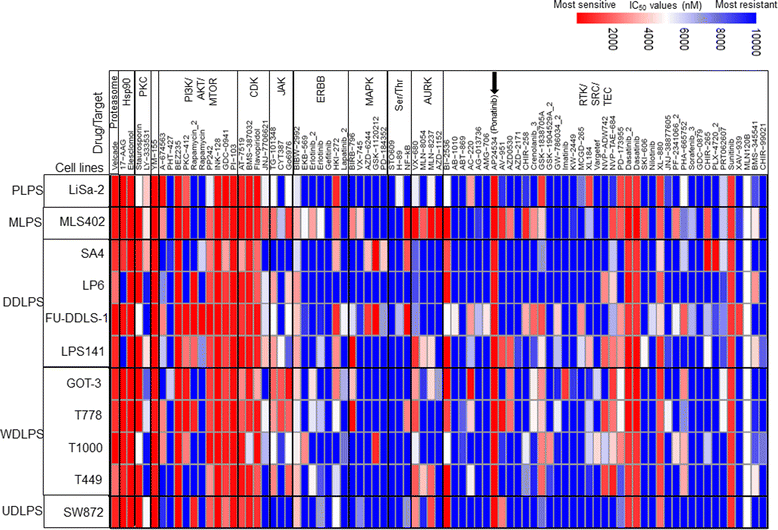




References
-
- Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Jones RL, Hensley ML, Schuetze SM, Staddon A, Milhem M, Elias A, Ganjoo K, Tawbi H, et al. Efficacy and safety of trabectedin or dacarbazine for metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma after failure of conventional chemotherapy: results of a phase III randomized multicenter clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:786–793. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.4734. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

