Vonoprazan treatment improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
- PMID: 29132551
- PMCID: PMC11915918
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kjms.2017.07.004
Vonoprazan treatment improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease
Abstract
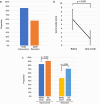
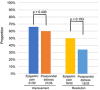
The effects of vonoprazan, a new potassium-competitive acid blocker, on gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) symptom are not fully elucidated. The aim of this study is to determine the effect of vonoprazan on GERD and associated gastrointestinal symptoms. We retrospectively reviewed 88 Helicobacter pylori negative patients with GERD treated with vonoprazan 10 mg daily. Symptoms were evaluated using the Izumo scale, which reflects quality of life related to various abdominal symptoms. The rates of improvement and resolution of GERD symptoms were 86% (76/88) and 57% (50/88), respectively. Improvement and resolution in patients with erosive esophagitis was higher than in those with non-erosive reflux disease (91% vs 83%, p = 0.260 and 71% vs 47%, p = 0.025, respectively). We attempted to identify factors which predict the effects of vonoprazan. Multivariate analysis identified advanced age (≥60-year-old) (odds ratio [OR] 7.281, 95% confidence interval [CI] 2.056-25.776, p = 0.002), obesity (BMI ≥ 24) (OR 3.342, 95%CI 1.124-9.940, p = 0.030) and erosive esophagitis (OR 4.368, 95%CI 1.281-14.895, p = 0.018) as positive predictors of resolution of GERD symptoms. Alcohol use (OR 0.131, 95%CI 0.027-0.632, p = 0.011) and history of H. pylori eradication (OR 0.171, 95%CI 0.041-0.718, p = 0.015) were identified as negative predictors. Vonoprazan also improved epigastric pain (73%), postprandial distress (60%), constipation (58%) and diarrhea (52%) in patients with GERD. In conclusion, vonoprazan 10 mg daily is effective in improving GERD symptoms. Advanced age, obesity, erosive esophagitis, alcohol use and history of H. pylori eradication influence the resolution of GERD symptoms. Treatment with vonoprazan favorably affects gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with GERD.
Keywords: Dyspepsia; Esophagitis; Gastroesophageal reflux disease; Outcome measure; Potassium-competitive acid blocker.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier Taiwan.
Figures
References
-
- Fujiwara Y., Arakawa T.. Epidemiology and clinical characteristics of GERD in the Japanese population. J Gastroenterol. 2009; 44: 518–534. - PubMed
-
- Dean B.B., Gano A.D. Jr., Knight K., Ofman J.J., Fass R.. Effectiveness of proton pump inhibitors in nonerosive reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2004; 2: 656–664. - PubMed
-
- Tack J., Fass R.. Review article: approaches to endoscopic‐negative reflux disease: part of the GERD spectrum or a unique acid‐related disorder?. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2004; 19 (Suppl. 1): 28–34. - PubMed
-
- Shimatani T., Sugimoto M., Nishino M., Adachi K., Furuta K., Ito M., et al. Predicting the efficacy of proton pump inhibitors in patients with non‐erosive reflux disease before therapy using dual‐channel 24‐h esophageal pH monitoring. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27: 899–906. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

