Closed-loop control of targeted ultrasound drug delivery across the blood-brain/tumor barriers in a rat glioma model
- PMID: 29133392
- PMCID: PMC5715774
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1713328114
Closed-loop control of targeted ultrasound drug delivery across the blood-brain/tumor barriers in a rat glioma model
Abstract
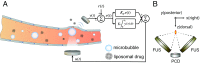
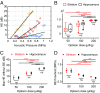
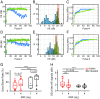
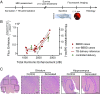
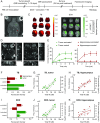
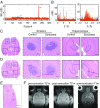
Cavitation-facilitated microbubble-mediated focused ultrasound therapy is a promising method of drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) for treating many neurological disorders. Unlike ultrasound thermal therapies, during which magnetic resonance thermometry can serve as a reliable treatment control modality, real-time control of modulated BBB disruption with undetectable vascular damage remains a challenge. Here a closed-loop cavitation controlling paradigm that sustains stable cavitation while suppressing inertial cavitation behavior was designed and validated using a dual-transducer system operating at the clinically relevant ultrasound frequency of 274.3 kHz. Tests in the normal brain and in the F98 glioma model in vivo demonstrated that this controller enables reliable and damage-free delivery of a predetermined amount of the chemotherapeutic drug (liposomal doxorubicin) into the brain. The maximum concentration level of delivered doxorubicin exceeded levels previously shown (using uncontrolled sonication) to induce tumor regression and improve survival in rat glioma. These results confirmed the ability of the controller to modulate the drug delivery dosage within a therapeutically effective range, while improving safety control. It can be readily implemented clinically and potentially applied to other cavitation-enhanced ultrasound therapies.
Keywords: acoustic cavitation; blood–brain barrier; drug delivery; focused ultrasound; treatment control.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Two provisional patents describing the controlling system and focused ultrasound system developed in this work have been filed (inventors: N.J.M. and T.S.). N.J.M. holds another two published patents on the ultrasound technique evaluated in this work. No conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

