Analysis of high-resolution 3D intrachromosomal interactions aided by Bayesian network modeling
- PMID: 29133398
- PMCID: PMC5715735
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1620425114
Analysis of high-resolution 3D intrachromosomal interactions aided by Bayesian network modeling
Abstract
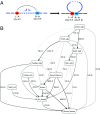
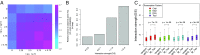
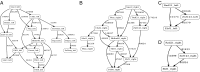
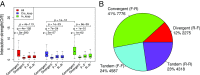
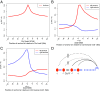
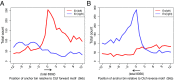
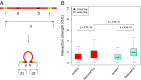
Long-range intrachromosomal interactions play an important role in 3D chromosome structure and function, but our understanding of how various factors contribute to the strength of these interactions remains poor. In this study we used a recently developed analysis framework for Bayesian network (BN) modeling to analyze publicly available datasets for intrachromosomal interactions. We investigated how 106 variables affect the pairwise interactions of over 10 million 5-kb DNA segments in the B-lymphocyte cell line GB12878. Strictly data-driven BN modeling indicates that the strength of intrachromosomal interactions (hic_strength) is directly influenced by only four types of factors: distance between segments, Rad21 or SMC3 (cohesin components),transcription at transcription start sites (TSS), and the number of CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF)-cohesin complexes between the interacting DNA segments. Subsequent studies confirmed that most high-intensity interactions have a CTCF-cohesin complex in at least one of the interacting segments. However, 46% have CTCF on only one side, and 32% are without CTCF. As expected, high-intensity interactions are strongly dependent on the orientation of the ctcf motif, and, moreover, we find that the interaction between enhancers and promoters is similarly dependent on ctcf motif orientation. Dependency relationships between transcription factors were also revealed, including known lineage-determining B-cell transcription factors (e.g., Ebf1) as well as potential novel relationships. Thus, BN analysis of large intrachromosomal interaction datasets is a useful tool for gaining insight into DNA-DNA, protein-DNA, and protein-protein interactions.
Keywords: DNA looping; DNA reeling; chromatin; enhancers.
Copyright © 2017 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dekker J, Rippe K, Dekker M, Kleckner N. Capturing chromosome conformation. Science. 2002;295:1306–1311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

