What Is Resistance? Impact of Phenotypic versus Molecular Drug Resistance Testing on Therapy for Multi- and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
- PMID: 29133554
- PMCID: PMC5786814
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01550-17
What Is Resistance? Impact of Phenotypic versus Molecular Drug Resistance Testing on Therapy for Multi- and Extensively Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis
Abstract
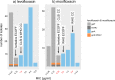
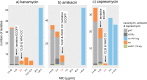
Rapid and accurate drug susceptibility testing (DST) is essential for the treatment of multi- and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (M/XDR-TB). We compared the utility of genotypic DST assays with phenotypic DST (pDST) using Bactec 960 MGIT or Löwenstein-Jensen to construct M/XDR-TB treatment regimens for a cohort of 25 consecutive M/XDR-TB patients and 15 possible anti-TB drugs. Genotypic DST results from Cepheid GeneXpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) and line probe assays (LPAs; Hain GenoType MTBDRplus 2.0 and MTBDRsl 2.0) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) were translated into individual algorithm-derived treatment regimens for each patient. We further analyzed if discrepancies between the various methods were due to flaws in the genotypic or phenotypic test using MIC results. Compared with pDST, the average agreement in the number of drugs prescribed in genotypic regimens ranged from just 49% (95% confidence interval [CI], 39 to 59%) for Xpert and 63% (95% CI, 56 to 70%) for LPAs to 93% (95% CI, 88 to 98%) for WGS. Only the WGS regimens did not contain any drugs to which pDST showed resistance. Importantly, MIC testing revealed that pDST likely underestimated the true rate of resistance for key drugs (rifampin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, and kanamycin) because critical concentrations (CCs) were too high. WGS can be used to rule in resistance even in M/XDR strains with complex resistance patterns, but pDST for some drugs is still needed to confirm susceptibility and construct the final regimens. Some CCs for pDST need to be reexamined to avoid systematic false-susceptible results in low-level resistant isolates.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; antibiotic resistance; molecular genetics.
Copyright © 2018 Heyckendorf et al.
Figures



Comment in
-
Whole-Genome Sequencing To Guide the Selection of Treatment for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jul 27;62(8):e00574-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00574-18. Print 2018 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30054376 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Dookie et al., "Whole-Genome Sequencing To Guide the Selection of Treatment for Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis".Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018 Jul 27;62(8):e00616-18. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00616-18. Print 2018 Aug. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018. PMID: 30054377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. 2016. Global tuberculosis report. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/250441/1/9789241565394-eng.pdf?....
-
- Lange C, Abubakar I, Alffenaar JWC, Bothamley G, Caminero Ja Carvalho ACC, Chang KC, Codecasa L, Correia A, Crudu V, Davies P, Dedicoat M, Drobniewski F, Duarte R, Ehlers C, Erkens C, Goletti D, Günther G, Ibraim E, Kampmann B, Kuksa L, De Lange W, Van Leth F, Van Lunzen J, Matteelli A, Menzies D, Monedero I, Richter E, Rüsch-Gerdes S, Sandgren A, Scardigli A, Skrahina A, Tortoli E, Volchenkov G, Wagner D, Van Der Werf MJ, Williams B, Yew WW, Zellweger JP, Cirillo DM. 2014. Management of patients with multidrugresistant/extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in Europe: a TBNET consensus statement. Eur Respir J 44:23–63. doi:10.1183/09031936.00188313. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Köser CU, Ellington MJ, Cartwright EJ, Gillespie SH, Brown NM, Farrington M, Holden MT, Dougan G, Bentley SD, Parkhill J, Peacock SJ. 2012. Routine use of microbial whole genome sequencing in diagnostic and public health microbiology. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002824. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

