NitroSynapsin therapy for a mouse MEF2C haploinsufficiency model of human autism
- PMID: 29133852
- PMCID: PMC5684358
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01563-8
NitroSynapsin therapy for a mouse MEF2C haploinsufficiency model of human autism
Abstract
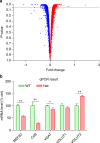
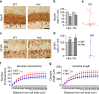
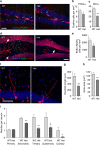
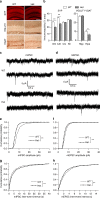
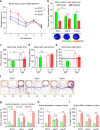
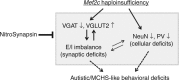
Transcription factor MEF2C regulates multiple genes linked to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), and human MEF2C haploinsufficiency results in ASD, intellectual disability, and epilepsy. However, molecular mechanisms underlying MEF2C haploinsufficiency syndrome remain poorly understood. Here we report that Mef2c +/-(Mef2c-het) mice exhibit behavioral deficits resembling those of human patients. Gene expression analyses on brains from these mice show changes in genes associated with neurogenesis, synapse formation, and neuronal cell death. Accordingly, Mef2c-het mice exhibit decreased neurogenesis, enhanced neuronal apoptosis, and an increased ratio of excitatory to inhibitory (E/I) neurotransmission. Importantly, neurobehavioral deficits, E/I imbalance, and histological damage are all ameliorated by treatment with NitroSynapsin, a new dual-action compound related to the FDA-approved drug memantine, representing an uncompetitive/fast off-rate antagonist of NMDA-type glutamate receptors. These results suggest that MEF2C haploinsufficiency leads to abnormal brain development, E/I imbalance, and neurobehavioral dysfunction, which may be mitigated by pharmacological intervention.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that S.A.L. is the inventor on worldwide patents for the use of memantine and NitroSynapsin for neurodegenerative and neurodevelopmental disorders. Per Harvard University guidelines, S.A.L. participates in a royalty-sharing agreement with his former institution Boston Children’s Hospital/Harvard Medical School, which licensed the drug memantine (Namenda®) to Forest Laboratories, Inc./Actavis/Allergan, Inc. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

