Relax, Cool Down and Scaffold: How to Restore Surface Expression of Folding-Deficient Mutant GPCRs and SLC6 Transporters
- PMID: 29135937
- PMCID: PMC5713384
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18112416
Relax, Cool Down and Scaffold: How to Restore Surface Expression of Folding-Deficient Mutant GPCRs and SLC6 Transporters
Abstract
Many diseases arise from mutations, which impair protein folding. The study of folding-deficient variants of G protein-coupled receptors and solute carrier 6 (SLC6) transporters has shed light on the folding trajectory, how it is monitored and how misfolding can be remedied. Reducing the temperature lowers the energy barrier between folding intermediates and thereby eliminates stalling along the folding trajectory. For obvious reasons, cooling down is not a therapeutic option. One approach to rescue misfolded variants is to use membrane-permeable orthosteric ligands. Antagonists of GPCRs are-in many instances-effective pharmacochaperones: they restore cell surface expression provided that they enter cells and bind to folding intermediates. Pharmacochaperoning of SLC6 transporters is less readily achieved because the ionic conditions in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) are not conducive to binding of typical inhibitors. The second approach is to target the heat-shock protein (HSP) relay, which monitors the folding trajectory on the cytosolic side. Importantly, orthosteric ligands and HSP-inhibitors are not mutually exclusive. In fact, pharmacochaperones and HSP-inhibitors can act in an additive or synergistic manner. This was exemplified by rescuing disease-causing, folding-deficient variants of the human dopamine transporters with the HSP70 inhibitor pifithrin-μ and the pharmacochaperone noribogaine in Drosophila melanogaster.
Keywords: G protein coupled receptors/GPCRs; heat-shock protein inhibitors; heat-shock protein relay; misfolding; pharmacochaperoning; solute carrier 6/SLC6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
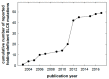
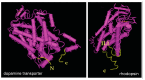
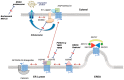
References
-
- Van Goor F., Hadida S., Grootenhuis P.D., Burton B., Stack J.H., Straley K.S., Decker C.J., Miller M., McCartney J., Olson E.R., et al. Correction of the F508del-CFTR protein processing defect in vitro by the investigational drug VX-809. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:18843–18848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105787108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

