A 17-molecule set as a predictor of complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil in esophageal cancer
- PMID: 29136005
- PMCID: PMC5685591
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188098
A 17-molecule set as a predictor of complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel, cisplatin, and 5-fluorouracil in esophageal cancer
Abstract
Background: Recently, neoadjuvant chemotherapy with docetaxel/cisplatin/5-fluorouracil (NAC-DCF) was identified as a novel strong regimen with a high rate of pathological complete response (pCR) in advanced esophageal cancer in Japan. Predicting pCR will contribute to the therapeutic strategy and the prevention of surgical invasion. However, a predictor of pCR after NAC-DCF has not yet been developed. The aim of this study was to identify a novel predictor of pCR in locally advanced esophageal cancer treated with NAC-DCF.
Patients and methods: A total of 32 patients who received NAC-DCF followed by esophagectomy between June 2013 and March 2016 were enrolled in this study. We divided the patients into the following 2 groups: pCR group (9 cases) and non-pCR group (23 cases), and compared gene expressions between these groups using DNA microarray data and KeyMolnet. Subsequently, a validation study of candidate molecular expression was performed in 7 additional cases.
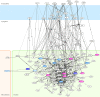
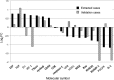
Results: Seventeen molecules, including transcription factor E2F, T-cell-specific transcription factor, Src (known as "proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase of sarcoma"), interferon regulatory factor 1, thymidylate synthase, cyclin B, cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4, CDK, caspase-1, vitamin D receptor, histone deacetylase, MAPK/ERK kinase, bcl-2-associated X protein, runt-related transcription factor 1, PR domain zinc finger protein 1, platelet-derived growth factor receptor, and interleukin 1, were identified as candidate molecules. The molecules were mainly associated with pathways, such as transcriptional regulation by SMAD, RB/E2F, and STAT. The validation study indicated that 12 of the 17 molecules (71%) matched the trends of molecular expression.
Conclusions: A 17-molecule set that predicts pCR after NAC-DCF for locally advanced esophageal cancer was identified.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Medical Research Council Oesophageal Cancer Working Party. Surgical resection with or without preoperative chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002;359:1727–1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)08651-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tanaka E, Okabe H, Tsunoda S, Obama K, Kan T, Kadokawa Y, et al. Feasibility of thoracoscopic esophagectomy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2012;5:111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1758-5910.2012.00131.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:11–20. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa055531 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ychou M, Boige V, Pignon JP, Conroy T, Bouche O, Lebreton G, et al. Perioperative chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma: an FNCLCC and FFCD multicenter phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:1715–1721. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.33.0597 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kitagawa Y, Idani H, Inoue H, Udagawa H, Uyama I, Osugi H, et al. Gastroenterological surgery: esophagus. Asian J Endosc Surg. 2015;8:114–124. doi: 10.1111/ases.12185 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

