Randomized, Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Duloxetine Versus Placebo for Aromatase Inhibitor-Associated Arthralgias in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: SWOG S1202
- PMID: 29136387
- PMCID: PMC5805479
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2017.74.6651
Randomized, Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial of Duloxetine Versus Placebo for Aromatase Inhibitor-Associated Arthralgias in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: SWOG S1202
Abstract
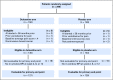
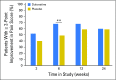
Purpose Adherence to aromatase inhibitor (AI) therapy for early-stage breast cancer is limited by AI-associated musculoskeletal symptoms (AIMSS). Duloxetine is US Food and Drug Administration approved for treatment of multiple chronic pain disorders. We hypothesized that treatment of AIMSS with duloxetine would improve average joint pain compared with placebo. Methods This randomized, double-blind, phase III trial included AI-treated postmenopausal women with early-stage breast cancer and who had average joint pain score of ≥ 4 out of 10 that developed or worsened since AI therapy initiation. Patients were randomly assigned 1:1 to duloxetine or placebo for 13 weeks. The primary end point was average joint pain through 12 weeks, examined using multivariable linear mixed models, adjusted for stratification factors (baseline pain score of 4 to 6 v 7 to 10 and prior taxane use). Clinically significant change in average pain was defined as a ≥ 2-point decrease from baseline. Results Of 299 enrolled patients, 127 patients treated with duloxetine and 128 who received placebo were evaluable for the primary analysis. By 12 weeks, the average joint pain score was 0.82 points lower for patients who received duloxetine compared with those who received placebo (95% CI, -1.24 to -0.40; P = .0002). Similar patterns were observed for worst joint pain, joint stiffness, pain interference, and functioning. Rates of adverse events of any grade were higher in the duloxetine-treated group (78% v 50%); rates of grade 3 adverse events were similar. Conclusion Results of treatment with duloxetine for AIMSS were superior to those of placebo among women with early-stage breast cancer, although it resulted in more frequent low-grade toxicities.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01598298.
Figures

Comment in
-
What Is the Role of Symptom Management and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Adherence to Aromatase Inhibitors?J Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb 1;36(4):308-309. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.76.3250. Epub 2017 Dec 15. J Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29244529 No abstract available.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG) : Aromatase inhibitors versus tamoxifen in early breast cancer: Patient-level meta-analysis of the randomised trials. Lancet 386:1341-1352, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Crew KD, Greenlee H, Capodice J, et al. : Prevalence of joint symptoms in postmenopausal women taking aromatase inhibitors for early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:3877-3883, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Crew KD, Capodice JL, Greenlee H, et al. : Randomized, blinded, sham-controlled trial of acupuncture for the management of aromatase inhibitor-associated joint symptoms in women with early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:1154-1160, 2010 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UG1 CA189971/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189873/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA233178/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA210962/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA210963/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189823/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189854/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189853/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189808/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189957/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189953/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180868/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189829/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189960/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189804/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189856/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180835/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189816/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180801/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189848/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189872/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189822/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189952/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA190002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189830/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189954/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180818/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189972/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

