A 4-miRNA signature to predict survival in glioblastomas
- PMID: 29136645
- PMCID: PMC5685622
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188090
A 4-miRNA signature to predict survival in glioblastomas
Abstract
Glioblastomas are among the most lethal cancers; however, recent advances in survival have increased the need for better prognostic markers. microRNAs (miRNAs) hold great prognostic potential being deregulated in glioblastomas and highly stable in stored tissue specimens. Moreover, miRNAs control multiple genes representing an additional level of gene regulation possibly more prognostically powerful than a single gene. The aim of the study was to identify a novel miRNA signature with the ability to separate patients into prognostic subgroups. Samples from 40 glioblastoma patients were included retrospectively; patients were comparable on all clinical aspects except overall survival enabling patients to be categorized as short-term or long-term survivors based on median survival. A miRNome screening was employed, and a prognostic profile was developed using leave-one-out cross-validation. We found that expression patterns of miRNAs; particularly the four miRNAs: hsa-miR-107_st, hsa-miR-548x_st, hsa-miR-3125_st and hsa-miR-331-3p_st could determine short- and long-term survival with a predicted accuracy of 78%. Heatmap dendrograms dichotomized glioblastomas into prognostic subgroups with a significant association to survival in univariate (HR 8.50; 95% CI 3.06-23.62; p<0.001) and multivariate analysis (HR 9.84; 95% CI 2.93-33.06; p<0.001). Similar tendency was seen in The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) using a 2-miRNA signature of miR-107 and miR-331 (miR sum score), which were the only miRNAs available in TCGA. In TCGA, patients with O6-methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) unmethylated tumors and low miR sum score had the shortest survival. Adjusting for age and MGMT status, low miR sum score was associated with a poorer prognosis (HR 0.66; 95% CI 0.45-0.97; p = 0.033). A Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes analysis predicted the identified miRNAs to regulate genes involved in cell cycle regulation and survival. In conclusion, the biology of miRNAs is complex, but the identified 4-miRNA expression pattern could comprise promising biomarkers in glioblastoma stratifying patients into short- and long-term survivors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

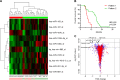
Similar articles
-
A 4-miRNAs signature predicts survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients.Cancer Biomark. 2017 Dec 6;20(4):443-452. doi: 10.3233/CBM-170205. Cancer Biomark. 2017. PMID: 28869437
-
miRNA array screening reveals cooperative MGMT-regulation between miR-181d-5p and miR-409-3p in glioblastoma.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):28195-206. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8618. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27057640 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression patterns in the malignant progression of gliomas and a 5-microRNA signature for prognosis.Oncotarget. 2014 Dec 30;5(24):12908-15. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2679. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25415048 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA signature in glioblastoma: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets.Exp Mol Pathol. 2020 Dec;117:104550. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104550. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Exp Mol Pathol. 2020. PMID: 33010295 Review.
-
Role of micro-RNA (miRNA) in pathogenesis of glioblastoma.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(9):1630-9. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26004603 Review.
Cited by
-
Developing an Immune-Related Signature for Predicting Survival Rate and the Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients With Glioma.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 2;13:899125. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.899125. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35719378 Free PMC article.
-
A 3-miRNA Signature Enables Risk Stratification in Glioblastoma Multiforme Patients with Different Clinical Outcomes.Curr Oncol. 2022 Jun 16;29(6):4315-4331. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29060345. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35735454 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of miRNA for the Treatment of MGMT Unmethylated Glioblastoma Multiforme.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 28;12(5):1099. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051099. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32354046 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning-Based Ensemble Recursive Feature Selection of Circulating miRNAs for Cancer Tumor Classification.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 3;12(7):1785. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071785. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32635415 Free PMC article.
-
Allele-Specific MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of a Glycolysis Gatekeeper PDK1 in Cancer Metabolism.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 17;13(14):3582. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143582. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. The Lancet Oncology. 2009;10(5):459–66. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. The New England journal of medicine. 2005;352(10):987–96. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043330 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Ellison DW, Figarella-Branger D, et al. WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system, Revised, 4th edition International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), Lyon: 2016.
-
- Delgado-Lopez PD, Corrales-Garcia EM. Survival in glioblastoma: a review on the impact of treatment modalities. Clinical & translational oncology: official publication of the Federation of Spanish Oncology Societies and of the National Cancer Institute of Mexico. 2016. Epub 2016/03/11. doi: 10.1007/s12094-016-1497-x . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kim VN, Han J, Siomi MC. Biogenesis of small RNAs in animals. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology. 2009;10(2):126–39. doi: 10.1038/nrm2632 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

