Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium, and association mapping analyses of Gossypium barbadense L. germplasm
- PMID: 29136656
- PMCID: PMC5685624
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188125
Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium, and association mapping analyses of Gossypium barbadense L. germplasm
Abstract
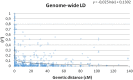
Limited polymorphism and narrow genetic base, due to genetic bottleneck through historic domestication, highlight a need for comprehensive characterization and utilization of existing genetic diversity in cotton germplasm collections. In this study, 288 worldwide Gossypium barbadense L. cotton germplasm accessions were evaluated in two diverse environments (Uzbekistan and USA). These accessions were assessed for genetic diversity, population structure, linkage disequilibrium (LD), and LD-based association mapping (AM) of fiber quality traits using 108 genome-wide simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Analyses revealed structured population characteristics and a high level of intra-variability (67.2%) and moderate interpopulation differentiation (32.8%). Eight percent and 4.3% of markers revealed LD in the genome of the G. barbadense at critical values of r2 ≥ 0.1 and r2 ≥ 0.2, respectively. The LD decay was on average 24.8 cM at the threshold of r2 ≥ 0.05. LD retained on average distance of 3.36 cM at the threshold of r2 ≥ 0.1. Based on the phenotypic evaluations in the two diverse environments, 100 marker loci revealed a strong association with major fiber quality traits using mixed linear model (MLM) based association mapping approach. Fourteen marker loci were found to be consistent with previously identified quantitative trait loci (QTLs), and 86 were found to be new unreported marker loci. Our results provide insights into the breeding history and genetic relationship of G. barbadense germplasm and should be helpful for the improvement of cotton cultivars using molecular breeding and omics-based technologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Campbell BT, Jones MA. Assessment of genotype × environment interactions for yield and fiber quality in cotton performance trials. Euphytica. 2005; 144:69–78. doi: 10.1007/s10681-005-4336-7 - DOI
-
- Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR. Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers reveal low levels of polymorphism between cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. Aust J Agric Res. 2005; 56:301–307. doi: 10.1071/AR04190 - DOI
-
- Culp TW, Harrell DC. Breeding methods for improving yield and fiber quality of Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Crop Sci. Madison, WI:Crop Science Society of America; 1973; 13:686–689. doi: 10.2135/cropsci1973.0011183X001300060030x - DOI
-
- Campbell BT, Saha S, Percy R, Frelichowski J, Jenkins JN, Park W, et al. Status of the global cotton germplasm resources. Crop Sci. 2010; 50:1161–1179. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2009.09.0551 - DOI
-
- Abdurakhmonov IY. World Cotton Germplasm Resources. 1st ed Rijeka:InTech Press; 2014. 320 p. doi: 10.5772/56978 https://www.intechopen.com/books/world-cotton-germplasm-resources - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

