Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer patients: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 29137007
- PMCID: PMC5690700
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008101
Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer patients: A meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer patients: A meta-analysis: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Jan;97(4):e9727. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009727. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29369210 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prognostic role of pretreatment neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in breast cancer patients: A meta-analysis: Erratum.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Dec;96(52):e9526. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009526. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 29384963 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Inflammation and cancer are closely related to each other. As a parameter that can reflect inflammation and host immune reaction, elevated blood neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) has been confirmed to be correlated with poor prognosis in a variety of cancers. However, this remains controversial in breast cancer. Thus, we performed this updated meta-analysis to further clarify whether high NLR could be a predictor of survival in breast cancer patients.
Methods: We searched on PubMed Database and Cochrane Library. Overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), and cancer-specific survival were used as outcome events, and hazard ratio (HR) was chosen as the parameter to evaluate the correlation.
Result: Eighteen eligible studies were involved in this meta-analysis. The synthesized analysis demonstrated that elevated NLR was associated with poor DFS [HR = 1.72, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) = 1.30-2.27], OS (HR = 1.87, 95% CI = 1.41-2.48), and cancer-specific survival (HR = 2.09, 95% CI = 1.04-4.21). The correlation was stronger in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) (OS: HR = 2.58, 95% CI = 1.63-4.06; DFS: HR = 3.51, 95% CI = 1.97-6.24).
Conclusion: Higher NLR was correlated to poor prognosis of breast cancer patients. As a clinical parameter that we can easily obtain, NLR might be a potential predictor in patients' survival to assist with physicians' treatment decisions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
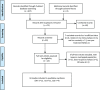
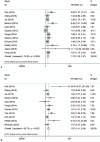
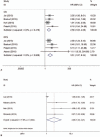
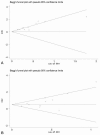
References
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Allen MD, Jones LJ. The role of inflammation in progression of breast cancer: friend or foe? (Review). Int J Oncol 2015;47:797–805. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

