Prognostic role of C-reactive protein in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis and literature review
- PMID: 29137033
- PMCID: PMC5690726
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008463
Prognostic role of C-reactive protein in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A meta-analysis and literature review
Abstract
Background: C-reactive protein (CRP) has been shown to be associated with several tumors. However, its association with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) is not well characterized. We performed a literature review and meta-analysis to assess the prognostic relevance of elevated CRP levels in patients with NPC.
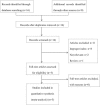
Methods: A literature search for relevant studies was performed on PubMed (Medline), the Cochrane Library, and Web of Science databases. Hazard ratios (95% confidence intervals) were calculated to assess the association between elevated CRP levels and survival outcomes.
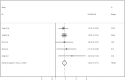
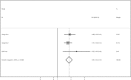
Results: Five studies with a combined study population of 5215 patients with NPC were included. Pooled hazard ratios for overall survival and distant metastasis-free survival were 1.84 (95% CI = 1.57-2.17) and 1.81 (95% CI = 1.53-2.14), respectively. Subgroup analyses showed that types of indicators and treatment before inclusion had no significant impact on the observed association.
Conclusion: Elevated serum CRP levels in patients with NPC were associated with worse prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wee J, Ha TC, Loong S, et al. Is nasopharyngeal cancer really a “Cantonese cancer”? Chin J Cancer 2010;29:517–26. - PubMed
-
- Chua MLK, Wee JTS, Hui EP, et al. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2016;387:1012–24. - PubMed
-
- Lu H, Peng L, Yuan X, et al. Concurrent chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a treatment paradigm also applicable to patients in Southeast Asia. Cancer Treat Rev 2009;35:345–53. - PubMed
-
- Wolden SL, Chen WC, Pfister DG, et al. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) for nasopharynx cancer: update of the Memorial Sloan-Kettering experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2006;64:57–62. - PubMed
-
- Gabay C, Kushner I. Acute-phase proteins and other systemic responses to inflammation. N Engl J Med 1999;340:448–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

