Functional characterization of lysine-specific demethylase 2 (LSD2/KDM1B) in breast cancer progression
- PMID: 29137219
- PMCID: PMC5669845
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19387
Functional characterization of lysine-specific demethylase 2 (LSD2/KDM1B) in breast cancer progression
Abstract
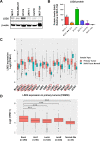
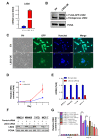
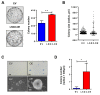
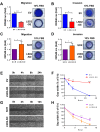
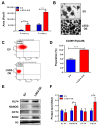
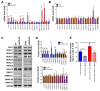
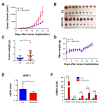
Flavin-dependent histone demethylases govern histone H3K4 methylation and act as important chromatin modulators that are extensively involved in regulation of DNA replication, gene transcription, DNA repair, and heterochromatin gene silencing. While the activities of lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1/KDM1A) in facilitating breast cancer progression have been well characterized, the roles of its homolog LSD2 (KDM1B) in breast oncogenesis are relatively less understood. In this study, we showed that LSD2 protein level was significantly elevated in malignant breast cell lines compared with normal breast epithelial cell line. TCGA- Oncomine database showed that LSD2 expression is significantly higher in basal-like breast tumors compared to other breast cancer subtypes or normal breast tissue. Overexpression of LSD2 in MDA-MB-231 cells significantly altered the expression of key important epigenetic modifiers such as LSD1, HDAC1/2, and DNMT3B; promoted cellular proliferation; and augmented colony formation in soft agar; while attenuating motility and invasion. Conversely, siRNA-mediated depletion of endogenous LSD2 hindered growth of multiple breast cancer cell lines while shRNA-mediated LSD2 depletion augmented motility and invasion. Moreover, LSD2 overexpression in MDA-MB-231 cells facilitated mammosphere formation, enriched the subpopulation of CD49f+/EpCAM- and ALDHhigh, and induced the expression of pluripotent stem cell markers, NANOG and SOX2. In xenograft studies using immune-compromised mice, LSD2-overexpressing MDA-MB-231 cells displayed accelerated tumor growth but significantly fewer lung metastases than controls. Taken together, our findings provide novel insights into the critical and multifaceted roles of LSD2 in the regulation of breast cancer progression and cancer stem cell enrichment.
Keywords: LSD2/KDM1B; breast cancer; cell growth; invasion; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of LSD1 and LSD2 in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System: An Update.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 17;12(3):462. doi: 10.3390/biom12030462. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of histone demethylase, LSD2 (KDM1B), attenuates DNA methylation and increases sensitivity to DNMT inhibitor-induced apoptosis in breast cancer cells.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Jul;146(1):99-108. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3012-9. Epub 2014 Jun 13. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 24924415
-
LSD2 Is an Epigenetic Player in Multiple Types of Cancer and Beyond.Biomolecules. 2024 May 3;14(5):553. doi: 10.3390/biom14050553. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Catalytic-Dependent and -Independent Roles of Lsd1 and Lsd2 Lysine Demethylases in Heterochromatin Formation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Cells. 2020 Apr 13;9(4):955. doi: 10.3390/cells9040955. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32295063 Free PMC article.
-
Functional interaction of histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5) and lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) promotes breast cancer progression.Oncogene. 2017 Jan 5;36(1):133-145. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.186. Epub 2016 May 23. Oncogene. 2017. PMID: 27212032 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Investigating the role of LSD2 as an epigenetic regulator in Ewing sarcoma.Oncotarget. 2019 Jun 11;10(39):3865-3878. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26988. eCollection 2019 Jun 11. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 31231465 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in H3K4me patterns due to aberrant expression of methyltransferases and demethylases in renal cell carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications.Sci Rep. 2019 Jun 3;9(1):8189. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-44733-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31160694 Free PMC article.
-
KDM1A Identified as a Potential Oncogenic Driver and Prognostic Biomarker via Multi-Omics Analysis.Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021 Dec 9;2021:4668565. doi: 10.1155/2021/4668565. eCollection 2021. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34925656 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of LSD1 and LSD2 in Cancers of the Gastrointestinal System: An Update.Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 17;12(3):462. doi: 10.3390/biom12030462. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35327654 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysine‑specific demethylase 2 contributes to the proliferation of small cell lung cancer by regulating the expression of TFPI‑2.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Jul;18(1):733-740. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9047. Epub 2018 May 22. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845195 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi Y. Histone lysine demethylases: emerging roles in development, physiology and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:829–33. - PubMed
-
- Højfeldt JW, Agger K, Helin K. Histone lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:917–30. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P, Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA, Shi Y. Histone demethylation mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell. 2004;119:941–53. - PubMed
-
- Garcia RN, D’Avila MF, Robe LJ, Loreto EL, Panzera Y, de Heredia FO, Valente VL. First evidence of methylation in the genome of Drosophila willistoni. Genetica. 2007;131:91–105. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

