miR-27a-3p targeting RXRα promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
- PMID: 29137318
- PMCID: PMC5669944
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19635
miR-27a-3p targeting RXRα promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway
Abstract
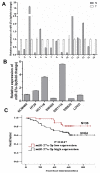
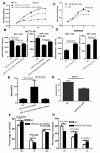
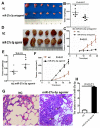
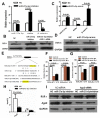
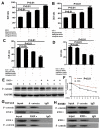
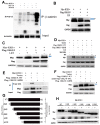
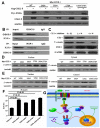
This study aimed to elucidate how miR-27a-3p modulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to promote colorectal cancer (CRC) progression. Our results showed that the expression of miR-27a-3p was up-regulated in CRC and closely associated with histological differentiation, clinical stage, distant metastasis and CRC patients' survival. miR-27a-3p mimic suppressed apoptosis and promoted proliferation, migration, invasion of CRC cells in vitro and in vivo. Whereas miR-27a-3p inhibitor promoted apoptosis and suppressed proliferation, migration, invasion of CRC cells in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, RXRα was the target gene of miR-27a-3p in CRC. miR-27a-3p expression negatively correlated with RXRα expression in CRC tissues. The underlining mechanism study showed that miR-27a-3p/RXRα/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in CRC progression. In conclusion, our findings first demonstrate that miR-27a-3p is a prognostic and/or potential therapeutic biomarker for CRC patients and RXRα as miR-27a-3p targeting gene plays an important role in activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway during CRC progression.
Keywords: RXRα; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; colorectal cancer; miR-27a-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chambon P. A decade of molecular biology of retinoic acid receptors. FASEB J. 1996;10:940–954. - PubMed
-
- Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM. The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell. 1995;83:841–850. - PubMed
-
- Heyman RA, Mangelsdorf DJ, Dyck JA, Stein RB, Eichele G, Evans RM, Thaller C. 9-cis retinoic acid is a high affinity ligand for the retinoid X receptor. Cell. 1992;68:397–406. - PubMed
-
- Mulholland DJ, Dedhar S, Coetzee GA, Nelson CC. Interaction of nuclear receptors with the Wnt/beta-catenin/Tcf signaling axis: Wnt you like to know? Endocr Rev. 2005;26:898–915. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

