Effects of growth hormone on cardiac remodeling and soleus muscle in rats with aortic stenosis-induced heart failure
- PMID: 29137319
- PMCID: PMC5669945
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.20583
Effects of growth hormone on cardiac remodeling and soleus muscle in rats with aortic stenosis-induced heart failure
Abstract
Background: Skeletal muscle wasting is often observed in heart failure (HF). The growth hormone (GH)/insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) axis is impaired in HF. In this study, we evaluated the effects of GH on soleus muscle and cardiac remodeling in rats with aortic stenosis (AS)-induced HF.
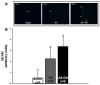
Methods: AS was created by placing a stainless-steel clip on the ascending aorta. After clinically detecting HF, GH (2 mg/kg/day) was subcutaneously injected for 14 days (AS-GH group). Results were compared with those from Sham and non-treated AS groups. Transthoracic echocardiogram was performed before and after treatment. Protein expression was evaluated by Western blot and satellite cells activation by immunofluorescence. Statistical analyzes: ANOVA and Tukey or Kruskal-Wallis and Student-Newman-Keuls.
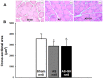
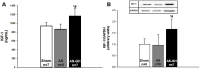
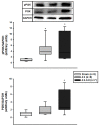
Results: Before treatment both AS groups presented a similar degree of cardiac injury. GH prevented body weight loss and attenuated systolic dysfunction. Soleus cross-sectional fiber areas were lower in both AS groups than Sham (Sham 3,556±447; AS 2,882±422; AS-GH 2,868±591 μm2; p=0.016). GH increased IGF-1 serum concentration (Sham 938±83; AS 866±116; AS-GH 1167±166 ng/mL; p<0.0001) and IGF-1 muscle protein expression and activated PI3K protein. Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) immunofluorescence was increased in both AS groups. Catabolism-related intracellular pathways did not differ between groups.
Conclusion: Short-term growth hormone attenuates left ventricular systolic dysfunction in rats with aortic stenosis-induced HF. Despite preserving body weight, increasing serum and muscular IGF-1 levels, and stimulating PI3K muscle expression, GH does not modulate soleus muscle trophism, satellite cells activation or intracellular pathways associated with muscle catabolism.
Keywords: growth hormone; heart failure; muscle trophicity; satellite cells; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors report no relationship that could be construed as a conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Growth hormone attenuates skeletal muscle changes in experimental chronic heart failure.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010 Apr;20(2):149-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2009.11.007. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2010. PMID: 20060348
-
Ventricular assist device implantation improves skeletal muscle function, oxidative capacity, and growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis signaling in patients with advanced heart failure.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2014 Dec;5(4):297-305. doi: 10.1007/s13539-014-0155-9. Epub 2014 Aug 7. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2014. PMID: 25100356 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone and heart failure: oxidative stress and energetic metabolism in rats.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008 Aug;18(4):275-83. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2007.11.002. Epub 2008 Jan 10. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2008. PMID: 18191600
-
Growth hormone and the insulin-like growth factor system in myogenesis.Endocr Rev. 1996 Oct;17(5):481-517. doi: 10.1210/edrv-17-5-481. Endocr Rev. 1996. PMID: 8897022 Review.
-
Role of growth hormone in chronic heart failure: therapeutic implications.Ital Heart J. 2000 Nov;1(11):732-8. Ital Heart J. 2000. PMID: 11110515 Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of physical exercise on microRNAs in skeletal muscle regeneration, aging and diseases.Oncotarget. 2018 Mar 30;9(24):17220-17237. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.24991. eCollection 2018 Mar 30. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29682218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of aerobic and resistance exercise on cardiac remodelling and skeletal muscle oxidative stress of infarcted rats.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 May;24(9):5352-5362. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15191. Epub 2020 Apr 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32239667 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Cachexia - A Window to the Wasting DisordersCardiac cachexia: perspectives for prevention and treatmentSkeletal muscle aging: influence of oxidative stress and physical exerciseCancer-induced muscle wasting: latest findings in prevention and treatmentCancer-induced cardiac cachexia: pathogenesis and impact of physical activity (Review)Muscle wasting and cachexia in heart failure: mechanisms and therapiesEffects of growth hormone on cardiac remodeling and soleus muscle in rats with aortic stenosis-induced heart failure.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018 Jan;110(1):102-103. doi: 10.5935/abc.20180009. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 29538532 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Fulster S, Tacke M, Sandek A, Ebner N, Tschope C, Doehner W, Anker SD, von Haehling S. Muscle wasting in patients with chronic heart failure: results from the studies investigating co-morbidities aggravating heart failure (SICA-HF) Eur Heart J. 2013;34:512–519. - PubMed
-
- Salomon F, Cuneo R, Sonksen PH. Growth hormone and protein metabolism. Horm Res. 1991;36:41–43. - PubMed
-
- Lewis AJ, Wester TJ, Burrin DG, Dauncey MJ. Exogenous growth hormone induces somatotrophic gene expression in neonatal liver and skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2000;278:R838–R844. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

