The role of indoxyl sulfate in renal anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 29137321
- PMCID: PMC5669947
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18789
The role of indoxyl sulfate in renal anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: The role of indoxyl sulfate in renal anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.Oncotarget. 2019 Mar 8;10(20):2006. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26782. eCollection 2019 Mar 8. Oncotarget. 2019. PMID: 30956780 Free PMC article.
Abstract
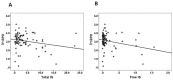
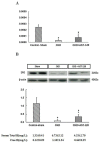
Renal anemia is a common complication in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. In vitro studies have shown that indoxyl sulfate decreases erythropoietin production. Whether this effect is seen in vivo remains unclear. Our goal was to explore the role of indoxyl sulfate in renal anemia. We found serum indoxyl sulfate levels are significantly and negatively associated with erythropoietin levels in human. A multiple stepwise linear regression analyses after adjustment for other independent parameters revealed that free indoxyl sulfate, and total indoxyl sulfate were significantly associated with erythropoietin levels. In animal studies, erythropoietin gene and protein expression were markedly inhibited in rats with chronic kidney disease; however, this effect was significantly reversed by lowering serum indoxyl sulfate with AST-120. Indoxyl sulfate may also inhibit erythropoietin expression in animal models with chronic kidney disease. These findings further support the role of indoxyl sulfate in the development of renal anemia.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; erythropoietin; indoxyl sulfate; renal anemia.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Nangaku M, Mimura I, Yamaguchi J, Higashijima Y, Wada T, Tanaka T. Role of uremic toxins in erythropoiesis-stimulating agent resistance in chronic kidney disease and dialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 2015;25:160–163. - PubMed
-
- Iseki K, Ikemiya Y, Iseki C, Takishita S. Haematocrit and the risk of developing end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:899–905. - PubMed
-
- Rossert J, Froissart M. Role of anemia in progression of chronic kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 2006;26:283–289. - PubMed
-
- Roth D, Smith RD, Schulman G, Steinman TI, Hatch FE, Rudnick MR, Sloand JA, Freedman BI, Williams WW, Jr, Shadur CA, Benz RL, Teehan BP, Revicki DA, et al. Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin on renal function in chronic renal failure predialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1994;24:777–784. - PubMed
-
- Kuriyama S, Tomonari H, Yoshida H, Hashimoto T, Kawaguchi Y, Sakai O. Reversal of anemia by erythropoietin therapy retards the progression of chronic renal failure, especially in nondiabetic patients. Nephron. 1997;77:176–185. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

