Prognostic value of PAM50 and risk of recurrence score in patients with early-stage breast cancer with long-term follow-up
- PMID: 29137653
- PMCID: PMC5686844
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-017-0911-9
Prognostic value of PAM50 and risk of recurrence score in patients with early-stage breast cancer with long-term follow-up
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic value of the PAM50 intrinsic subtypes and risk of recurrence (ROR) score in patients with early breast cancer and long-term follow-up. A special focus was placed on hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HR+/HER2-) pN0 patients not treated with chemotherapy.
Methods: Patients with early breast cancer (n = 653) enrolled in the observational Oslo1 study (1995-1998) were followed for distant recurrence and breast cancer death. Clinicopathological parameters were collected from hospital records. The primary tumors were analyzed using the Prosigna® PAM50 assay to determine the prognostic value of the intrinsic subtypes and ROR score in comparison with pathological characteristics. The primary endpoints were distant disease-free survival (DDFS) and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS).
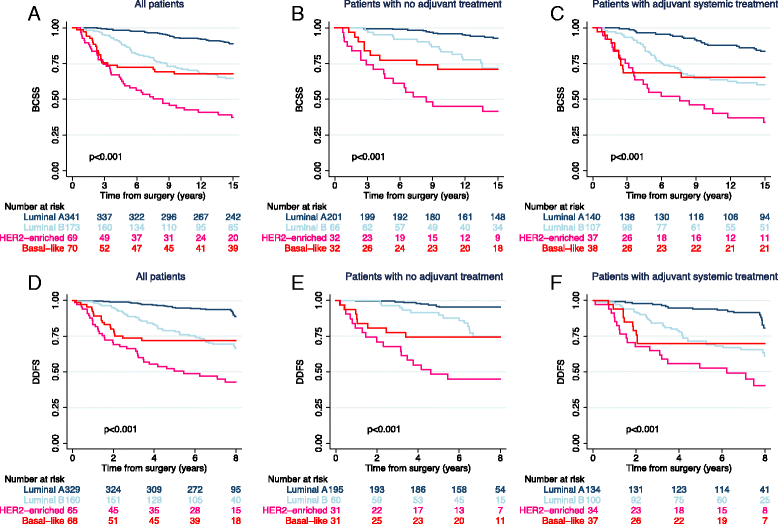
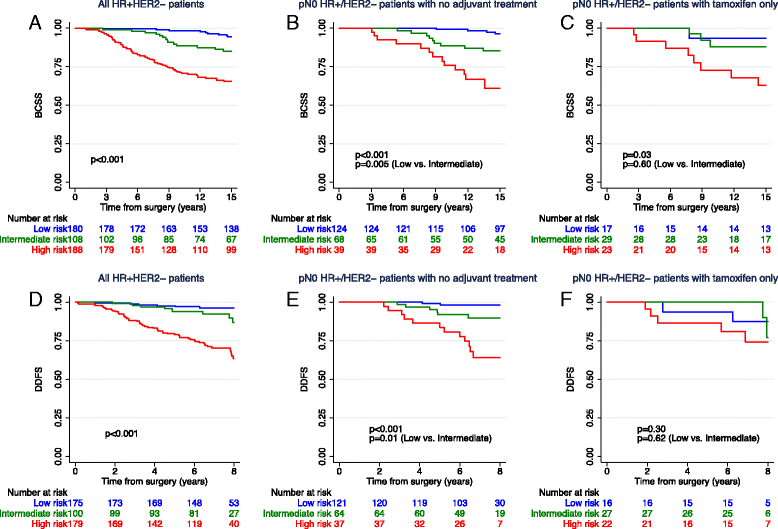
Results: Of 653 tumors, 52.2% were classified as luminal A, 26.5% as luminal B, 10.6% as HER2-enriched, and 10.7% as basal-like. Among the HR+/HER2- patients (n = 476), 37.8% were categorized as low risk by ROR score, 22.7% as intermediate risk, and 39.5% as high risk. Median follow-up durations for BCSS and DDFS were 16.6 and 7.1 years, respectively. Multivariate analysis showed that intrinsic subtypes (all patients) and ROR risk classification (HR+/HER2- patients) yielded strong prognostic information. Among the HR+/HER2- pN0 patients with no adjuvant treatment (n = 231), 53.7% of patients had a low ROR, and their prognosis at 15 years was excellent (15-year BCSS 96.3%). Patients with intermediate risk had reduced survival compared with those with low risk (p = 0.005). In contrast, no difference in survival between the low- and intermediate-risk groups was seen for HR+/HER2- pN0 patients who received tamoxifen only. Ki-67 protein, grade, and ROR score were analyzed in the unselected, untreated pT1pN0 HR+/HER2- population (n = 171). In multivariate analysis, ROR score outperformed both Ki-67 and grade. Furthermore, 55% of patients who according to the PREDICT tool ( http://www.predict.nhs.uk/ ) would be considered chemotherapy candidates were ROR low risk (33%) or luminal A ROR intermediate risk (22%).
Conclusions: The PAM50 intrinsic subtype classification and ROR score improve classification of patients with breast cancer into prognostic groups, allowing for a more precise identification of future recurrence risk and providing an improved basis for adjuvant treatment decisions. Node-negative patients with low ROR scores had an excellent outcome at 15 years even in the absence of adjuvant therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Follow-up; PAM50; Patient stratification; Risk of recurrence.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Norwegian Regional Committees for Medical and Health Research Ethics, REC South East (reference 2015/2453). Written consent was obtained from all patients.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365(9472):1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T, Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98(19):10869–10874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.191367098. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris LN, Ismaila N, McShane LM, Andre F, Collyar DE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hammond EH, Kuderer NM, Liu MC, Mennel RG, et al. Use of biomarkers to guide decisions on adjuvant systemic therapy for women with early-stage invasive breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(10):1134–1150. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.2289. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coates AS, Winer EP, Goldhirsch A, Gelber RD, Gnant M, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thurlimann B, Senn HJ. Tailoring therapies—improving the management of early breast cancer: St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2015. Ann Oncol. 2015;26(8):1533–1546. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

