Autonomic regulation of the immune system in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 29138216
- PMCID: PMC6105770
- DOI: 10.1152/advan.00061.2017
Autonomic regulation of the immune system in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
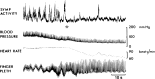
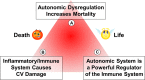
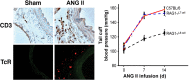
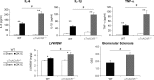
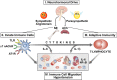
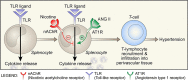
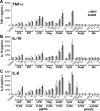
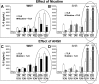
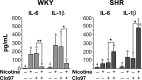
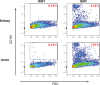
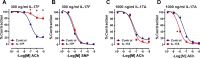
The autonomic nervous system is a powerful regulator of circulatory adjustments to acute hemodynamic stresses. Here we focus on new concepts that emphasize the chronic influence of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems on cardiovascular pathology. The autonomic neurohumoral system can dramatically influence morbidity and mortality from cardiovascular disease through newly discovered influences on the innate and adaptive immune systems. Specifically, the end-organ damage in heart failure or hypertension may be worsened or alleviated by pro- or anti-inflammatory pathways of the immune system, respectively, that are activated through neurohumoral transmitters. These concepts provide a major new perspective on potentially life-saving therapeutic interventions in the deadliest of diseases.
Keywords: cytokines; hypertension; immune system; parasympathetic; sympathetic.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures




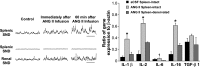







Similar articles
-
Role of Neuroendocrine, Immune, and Autonomic Nervous System in Anorexia Nervosa-Linked Cardiovascular Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 2;21(19):7302. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197302. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gender differences in the neurohumoral control of the cardiovascular system.Ital Heart J. 2003 Jun;4(6):367-70. Ital Heart J. 2003. PMID: 12898799 Review.
-
[Autonomic nervous system and sleep apnea syndromes].Rev Mal Respir. 2000 Jun;17 Suppl 3:S51-67. Rev Mal Respir. 2000. PMID: 10939104 Review. French.
-
Autonomic Cardiovascular Control and Executive Function in Chronic Hypotension.Ann Behav Med. 2017 Jun;51(3):442-453. doi: 10.1007/s12160-016-9868-7. Ann Behav Med. 2017. PMID: 27957701
-
Cardiovascular autonomic and hemodynamic responses to vagus nerve stimulation in drug-resistant epilepsy.Seizure. 2017 Feb;45:56-60. doi: 10.1016/j.seizure.2016.11.018. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Seizure. 2017. PMID: 27919011
Cited by
-
Regulatory T cells protected against abdominal aortic aneurysm by suppression of the COX-2 expression.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Oct;23(10):6766-6774. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14554. Epub 2019 Jul 21. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31328426 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term High-NaCl Dietary Intake Changes Leukocyte Expression of VLA-4, LFA-1, and Mac-1 Integrins in Both Healthy Humans and Sprague-Dawley Rats: A Comparative Study.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Sep 17;2019:6715275. doi: 10.1155/2019/6715275. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31636506 Free PMC article.
-
Four evolving concepts in molecular and clinical autonomic research.Clin Auton Res. 2021 Aug;31(4):467-471. doi: 10.1007/s10286-021-00816-3. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Clin Auton Res. 2021. PMID: 34191210 No abstract available.
-
Applications of Non-invasive Neuromodulation for the Management of Disorders Related to COVID-19.Front Neurol. 2020 Nov 25;11:573718. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.573718. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33324324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Response of Heart Rate Variability to Active Standing in Aortic Valve Disease: Insights from Recurrence Quantification Analysis.Sensors (Basel). 2025 Mar 1;25(5):1535. doi: 10.3390/s25051535. Sensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40096400 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abboud F, Thames MD, Mark AL. Role of cardiac afferent nerves in regulation of circulation during coronary occlusion and heart failure. In: Disturbances in Neurogenic Control of the Circulation, edited by Abboud FM, Fozzard HA, Gilmore JP, Reid DJ. Bethesda, MD: American Physiological Society, 1981, p. 65–86.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

