TALEN-mediated shift of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in MELAS-iPSCs with m.13513G>A mutation
- PMID: 29138463
- PMCID: PMC5686150
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-15871-y
TALEN-mediated shift of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in MELAS-iPSCs with m.13513G>A mutation
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: TALEN-mediated shift of mitochondrial DNA heteroplasmy in MELAS-iPSCs with m.13513 G>A mutation.Sci Rep. 2018 Mar 13;8(1):4683. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22721-y. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29535331 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are suitable for studying mitochondrial diseases caused by mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) mutations. Here, we generated iPSCs from a patient with mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like episodes (MELAS) with the m.13513G>A mutation. The patient's dermal fibroblasts were reprogrammed, and we established two iPSC clones with and without mutant mtDNA. Furthermore, we tried to decrease mutant mtDNA level in iPSCs using transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs). We originally engineered platinum TALENs, which were transported into mitochondria, recognized the mtDNA sequence including the m.13513 position, and preferentially cleaved G13513A mutant mtDNA (G13513A-mpTALEN). The m.13513G>A heteroplasmy level in MELAS-iPSCs was decreased in the short term by transduction of G13513A-mpTALEN. Our data demonstrate that this mtDNA-targeted nuclease would be a powerful tool for changing the heteroplasmy level in heteroplasmic iPSCs, which could contribute to elucidation of the pathological mechanisms of mitochondrial diseases caused by mtDNA mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
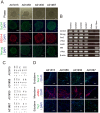
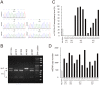
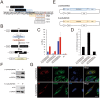
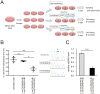
References
-
- Iizuka, T. & Sakai, F. Pathogenesis of stroke-like episodes in MELAS: analysis of neurovascular cellular mechanisms. Current neurovascular research2, 29–45, https://doi.org/10.2174/1567202052773544 (2005). - DOI - PubMed
-
- Takahashi, K. et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell131, 861–872, 10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019 (2007). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

