Role of innate lymphoid cells in obesity and metabolic disease (Review)
- PMID: 29138853
- PMCID: PMC5780078
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8038
Role of innate lymphoid cells in obesity and metabolic disease (Review)
Abstract
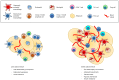
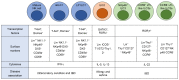
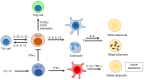
The immune system has previously been demonstrated to be associated with the pathophysiological development of metabolic abnormalities. However, the mechanisms linking immunity to metabolic disease remain to be fully elucidated. It has previously been suggested that innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) may be involved in the progression of numerous types of metabolic diseases as these cells act as suppressors and promoters for obesity and associated conditions, and are particularly involved in adipose tissue inflammation, which is a major feature of metabolic imbalance. Group 2 ILCs (ILC2s) have been revealed as anti‑obese immune regulators by secreting anti‑inflammatory cytokines and promoting the polarization of M2 macrophages, whereas group 1 ILCs (ILC1s), including natural killer cells, may promote adipose tissue inflammation via production of interferon‑γ, which in turn polarizes macrophages toward the M1 type. The majority of studies to date have demonstrated the pathological association between ILCs and obesity in the context of adipose tissue inflammation, whereas the roles of ILCs in other organs which participate in obesity development have not been fully characterized. Therefore, identifying the roles of all types of ILCs as central components mediating obesity‑associated inflammation, is of primary concern, and may lead to the discovery of novel preventative and therapeutic interventions.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

