17β-estradiol attenuates ovariectomy‑induced bone deterioration through the suppression of the ephA2/ephrinA2 signaling pathway
- PMID: 29138859
- PMCID: PMC5780101
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8042
17β-estradiol attenuates ovariectomy‑induced bone deterioration through the suppression of the ephA2/ephrinA2 signaling pathway
Abstract
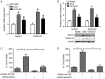
The present study aimed to investigate whether 17β‑estradiol (E2) exerts protective effects on bone deterioration induced by ovariectomy (OVX) through the ephA2/ephrinA2 signaling pathway in rats. Female rats were subjected to OVX, sham surgeryor OVX+E2 treatment. Levels of biomarkers were measured in serum and urine. Hematoxylin and eosin staining was performed on paraffin‑embedded bone sections. Expression of genes and proteins was analyzed by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting, respectively. Bone mineral density (BMD) was analyzed by dual‑energy X‑ray absorptiometry. Trabecular bone microarchitecture was also evaluated. Osteoclastogenesis was induced by in vitro culturing with mouse receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL) and macrophage colony‑stimulating factor 1. small interfering RNA was designed to knockdown ehpA2 receptor and its ligand ephrinA2. Results of the present study demonstrated that E2 had suppressive effects on OVX‑induced body weight gain and bone turnover factors in serum and urine. E2 inhibited the bone resorption function of osteoclasts by inhibiting the production of tartrate‑resistant acid phosphatase‑5b and RANKL, and induced bone formation function of osteoblasts by prompting runt‑related transcription factor 2, Sp7 transcription factor and collagen alpha‑1(I) chain expression in bone marrow cells. E2 treatment significantly increased the tibia BMD and prevented the deterioration of trabecular microarchitecture compared with the OVX group. Moreover, E2 significantly decreased the OVX‑stimulated expression of ephA2 and ephrinA2. EphA2 or ephrin A2 knockdown significantly suppressed osteoclastogenesis in vitro. In conclusion, E2 can attenuate OVX‑induced bone deterioration partially through the suppression of the ephA2/ephrinA2 signaling pathway. Therefore EphA2/ephrinA2 signaling pathway may be a potential target for osteoporosis treatment.
Figures




References
-
- Jin S, Yan Z, Yang T, Liu S, Liang W, Hui Y. Eph-ephrin bidirectional signalling: A promising approach for osteoporosis treatment. J Med Hypotheses Ideas. 2013;7:40–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jmhi.2013.02.002. - DOI
-
- Sarrel PM, Lufkin EG, Oursler MJ, Keefe D. Estrogen actions in arteries, bone and brain. Sci Med. 1994;1:44.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

