Design, synthesis, conformational and molecular docking study of some novel acyl hydrazone based molecular hybrids as antimalarial and antimicrobial agents
- PMID: 29138944
- PMCID: PMC5686033
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-017-0344-7
Design, synthesis, conformational and molecular docking study of some novel acyl hydrazone based molecular hybrids as antimalarial and antimicrobial agents
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Design, synthesis, conformational and molecular docking study of some novel acyl hydrazone based molecular hybrids as antimalarial and antimicrobial agents.Chem Cent J. 2018 Feb 6;12(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s13065-018-0374-9. Chem Cent J. 2018. PMID: 29411150 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Acyl hydrazones are an important class of heterocyclic compounds promising pharmacological characteristics. Malaria is a life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease caused by a plasmodium parasite. In some places, malaria can be treated and controlled with early diagnosis. However, some countries lack the resources to do this effectively.
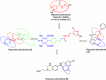
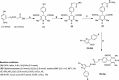
Results: The present work involves the design and synthesis of some novel acyl hydrazone based molecular hybrids of 1,4-dihydropyridine and pyrazole (5a-g). These molecular hybrids were synthesised by condensation of 1,4-dihydropyridin-4-yl-phenoxyacetohydrazides with differently substituted pyrazole carbaldehyde. The final compound (5) showed two conformations (the major, E, s-cis and the minor, E, s-trans) as revealed by NMR spectral data and further supported by the energy calculations (MOPAC2016 using PM7 method). All the synthesised compounds were screened for their in vitro antimalarial activities against chloroquine-sensitive malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum (3D7) and antimicrobial activity against Gram positive bacteria i.e. Bacillus cereus, Gram negative bacteria i.e. Escherichia coli and antifungal activity against one fungus i.e. Aspergillus niger [corrected]. All these compounds were found more potent than chloroquine and clotrimazole, the standard drugs.
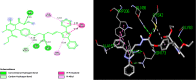
Conclusions: In vitro antiplasmodial IC50 value of the most potent compound 5d was found to be 4.40 nM which is even less than all the three reference drugs chloroquine (18.7 nM), pyrimethamine (11 nM) and artimisinin (6 nM). In silico binding study of compound 5d with plasmodial cysteine protease falcipain-2 indicated the inhibition of falcipain-2 as the probable reason for the antimalarial potency of compound 5d. All the compounds had shown good to excellent antimicrobial and antifungal activities.
Keywords: Antifungal; Antimalarial; Antimicrobial; Conformational studies; DHP; Falcipain-2; Plasmodium falciparum; Pyrazole.
Figures
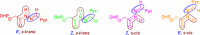



References
-
- World Malaria Report 2014 (2014) World Health Organization
-
- Alílio MS, Bygbjerg IC, Breman JG. Are multilateral malarial research and control programs the most successful? Lessons from the past 100 years in Africa. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;71:268–278. - PubMed
-
- Tumwebaze P, Conrad MD, Walakira A, LeClair N, Byaruhanga O, Nakazibwe C, Kozak B, Bloome J, Okiring J, Kakuru A, Bigira V, Kapisi J, Legac J, Gut J, Cooper RA, Kamya MR, Havlir DV, Dorsey G, Greenhouse B, Nsobya SL, Rosenthal PJ. Impact of antimalarial treatment and chemoprevention on the drug sensitivity of malaria parasites isolated from Ugandan children. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2015;59:3018–3030. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05141-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

