Immune checkpoint inhibitors: new strategies to checkmate cancer
- PMID: 29139554
- PMCID: PMC5758374
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13081
Immune checkpoint inhibitors: new strategies to checkmate cancer
Abstract
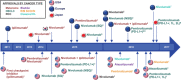
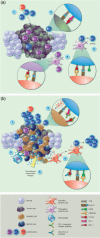
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) targeting cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated protein-4 (CTLA-4) or programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) receptors have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in subsets of patients with malignant disease. This emerging treatment modality holds great promise for future cancer treatment and has engaged pharmaceutical research interests in tumour immunology. While ICIs can induce rapid and durable responses in some patients, identifying predictive factors for effective clinical responses has proved challenging. This review summarizes the mechanisms of action of ICIs and outlines important preclinical work that contributed to their development. We explore clinical data that has led to disease-specific drug licensing, and highlight key clinical trials that have revealed ICI efficacy across a range of malignancies. We describe how ICIs have been used as part of combination therapies, and explore their future prospects in this area. We conclude by discussing the incorporation of these new immunotherapeutics into precision approaches to cancer therapy.
Keywords: T cell; antibodies; cancer; tumour immunology.
© 2017 British Society for Immunology.
Figures
References
-
- Speiser DE, Ho PC, Verdeil G. Regulatory circuits of T cell function in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol 2016; 16:599–611. - PubMed
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The immunobiology of cancer immunosurveillance and immunoediting. Immunity 2004; 21:137–48. - PubMed
-
- Prendergast GC. Immune escape as a fundamental trait of cancer: focus on IDO. Oncogene 2008; 27:3889–900. - PubMed
-
- Igney FH, Krammer PH. Immune escape of tumors: apoptosis resistance and tumor counterattack. J Leukoc Biol 2002; 71:907–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

