Host Methyltransferases and Demethylases: Potential New Epigenetic Targets for HIV Cure Strategies and Beyond
- PMID: 29140109
- PMCID: PMC5684665
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2017.0180
Host Methyltransferases and Demethylases: Potential New Epigenetic Targets for HIV Cure Strategies and Beyond
Abstract
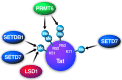
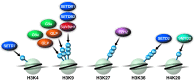
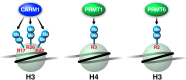
A successful HIV cure strategy may require reversing HIV latency to purge hidden viral reservoirs or enhancing HIV latency to permanently silence HIV transcription. Epigenetic modifying agents show promise as antilatency therapeutics in vitro and ex vivo, but also affect other steps in the viral life cycle. In this review, we summarize what we know about cellular DNA and protein methyltransferases (PMTs) as well as demethylases involved in HIV infection. We describe the biology and function of DNA methyltransferases, and their controversial role in HIV infection. We further explain the biology of PMTs and their effects on lysine and arginine methylation of histone and nonhistone proteins. We end with a focus on protein demethylases, their unique modes of action and their emerging influence on HIV infection. An outlook on the use of methylation-modifying agents in investigational HIV cure strategies is provided.
Keywords: HIV cure; demethylase inhibitors; histone demethylase; latency reactivation; methyltransferase; methyltransferase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
