IL-21 Therapy Controls Immune Activation and Maintains Antiviral CD8+ T Cell Responses in Acute Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
- PMID: 29140110
- PMCID: PMC5684667
- DOI: 10.1089/aid.2017.0160
IL-21 Therapy Controls Immune Activation and Maintains Antiviral CD8+ T Cell Responses in Acute Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Infection
Abstract
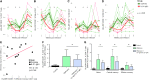
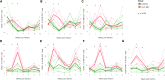
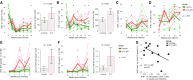
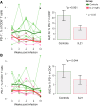
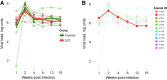
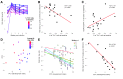
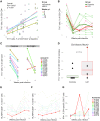
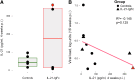
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) replicate during acute infection in lymphocytes of the gastrointestinal tract, before disseminating systemically. Localized replication and associated loss of gut-resident CD4+ T cells occur regardless of the portal of entry of the virus (e.g., intravenous vs. rectal). Thus, HIV and SIV are tropic for gut tissue, and their pathogenesis requires the special environment of the intestine. T helper 17 (Th17) cells are important contributors to microbial defense in the gut that are vulnerable to HIV infection and whose loss is associated with translocation of microbial products to the systemic circulation, leading to chronic immune activation and disease progression. Interleukin (IL)-21 promotes differentiation and survival of Th17 cells and stimulates CD8+ T cell function. By promoting Th17 cell survival, IL-21 could limit bacterial translocation and immune activation in the setting of acute or rebounding HIV/SIV disease. In this study, we tested the effect of recombinant IL-21-IgFc treatment, given at the time of infection, on SIVmac251 infection. We found that rIL-21-IgFc decreases immune activation and maintains effective antiviral responses by CD8+ T cells in blood, but this maintenance is not associated with lower viral loads. rIL-21-IgFc treatment also did not generally support Th17 cell populations, but Th17 cells remained strongly and independently associated with control of plasma viremia. For example, the single animal exhibiting greatest control over viremia in our study also manifested the highest levels of IL-21 in plasma, Th17 cell maintenance in blood, and Th17 cells in intestinal tissue. These findings provide rationale for further exploration of IL-21 treatment as a support for host CD8+ T cell responses in HIV cure strategies.
Keywords: SIV; Th17; cure; immune activation; interleukin-21; rhesus macaques.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Brenchley JM, Price DA, Schacker TW, Asher TE, Silvestri G, Rao S, et al. : Microbial translocation is a cause of systemic immune activation in chronic HIV infection. Nat Med 2006;12:1365–1371 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

