Dissecting human ILC heterogeneity: more than just three subsets
- PMID: 29140572
- PMCID: PMC5795188
- DOI: 10.1111/imm.12862
Dissecting human ILC heterogeneity: more than just three subsets
Abstract
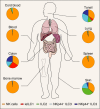
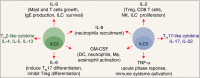
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) have been divided into three distinct groups based on functional capacities, cytokine profiles and transcription factor expression. Studies performed mainly in mice have demonstrated the importance of ILCs in chronic inflammation, infection, allergy and cancer. In this review, we discuss the heterogeneity of human ILC and focus primarily on the taxonomy of human ILC cell subsets and their phenotypical and functional diversity. We summarize recent findings concerning the diversity of ILCs between and within the major subsets [natural killer (NK), ILC1, intra-epithelial ILC1 (ieILC1), ILC2, ILC3, lymphoid tissues inducer (LTi) and ILC progenitor (ILCP)], as well as the abundance of each in human tissues. We also discuss the similarities observed between groups of cells in term of receptors expressed and cytokines produced, and how these relate to the pleiotropic properties of each subset.
Keywords: ILC1; ILC2; ILC3; heterogeneity; human; ieILC1.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Spits H, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G et al Innate lymphoid cells – a proposal for uniform nomenclature. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13:145–9. - PubMed
-
- Satoh‐Takayama N, Vosshenrich CA, Lesjean‐Pottier S, Sawa S, Lochner M, Rattis F et al Microbial flora drives interleukin 22 production in intestinal NKp46+ cells that provide innate mucosal immune defense. Immunity 2008; 29:958–70. - PubMed
-
- Artis D, Spits H. The biology of innate lymphoid cells. Nature 2015; 517:293–301. - PubMed
-
- Bernink JH, Krabbendam L, Germar K, de Jong E, Gronke K, Kofoed‐Nielsen M et al Interleukin‐12 and ‐23 control plasticity of CD127(+) group 1 and group 3 innate lymphoid cells in the intestinal lamina propria. Immunity 2015; 43:146–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

