Collagen Alignment as a Predictor of Recurrence after Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
- PMID: 29141852
- PMCID: PMC5809285
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0720
Collagen Alignment as a Predictor of Recurrence after Ductal Carcinoma In Situ
Abstract
Background: Collagen fibers surrounding breast ducts may influence breast cancer progression. Syndecan-1 interacts with constituents in the extracellular matrix, including collagen fibers, and may contribute to cancer cell migration. Thus, the orientation of collagen fibers surrounding ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) lesions and stromal syndecan-1 expression may predict recurrence.Methods: We evaluated collagen fiber alignment and syndecan-1 expression in 227 women diagnosed with DCIS in 1995 to 2006 followed through 2014 (median, 14.5 years; range, 0.7-17.6). Stromal collagen alignment was evaluated from diagnostic tissue slides using second harmonic generation microscopy and fiber analysis software. Univariate analysis was conducted using χ2 tests and ANOVA. The association between collagen alignment z-scores, syndecan-1 staining intensity, and time to recurrence was evaluated using HRs and 95% confidence intervals (CIs).Results: Greater fiber angles surrounding DCIS lesions, but not syndecan-1 staining intensity, were related to positive HER2 (P = 0.002) status, comedo necrosis (P = 0.03), and negative estrogen receptor (P = 0.002) and progesterone receptor (P = 0.02) status. Fiber angle distributions surrounding lesions included more angles closer to 90 degrees than normal ducts (P = 0.06). Collagen alignment z-scores for DCIS lesions were positively related to recurrence (HR = 1.25; 95% CI, 0.84-1.87 for an interquartile range increase in average fiber angles).Conclusions: Although collagen alignment and stromal syndecan-1 expression did not predict recurrence, collagen fibers perpendicular to the duct perimeter were more frequent in DCIS lesions with features typical of poor prognosis.Impact: Follow-up studies are warranted to examine whether additional features of the collagen matrix may more strongly predict patient outcomes. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev; 27(2); 138-45. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


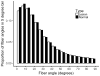
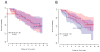

Comment in
-
Collagen Alignment and Recurrence of DCIS-Letter.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2018 May;27(5):613. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-1071. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2018. PMID: 29716929 No abstract available.
References
-
- Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Kosary CL, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2014. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: Apr, 2017. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2014/, based on November 2016 SEER data submission, posted to the SEER web site.
-
- Sprague BL, Trentham-Dietz A. In situ Breast Cancer. In: Li CI, editor. Breast Cancer Epidemiology. New York: Springer; 2010. pp. 47–72.
-
- Warnberg F, Yuen J, Holmberg L. Risk of subsequent invasive breast cancer after breast carcinoma in situ. Lancet. 2000;355:724–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

