Interleukin-1 Blockade in Recently Decompensated Systolic Heart Failure: Results From REDHART (Recently Decompensated Heart Failure Anakinra Response Trial)
- PMID: 29141858
- PMCID: PMC5699505
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.117.004373
Interleukin-1 Blockade in Recently Decompensated Systolic Heart Failure: Results From REDHART (Recently Decompensated Heart Failure Anakinra Response Trial)
Abstract
Background: An enhanced inflammatory response predicts worse outcomes in heart failure (HF). We hypothesized that administration of IL-1 (interleukin-1) receptor antagonist (anakinra) could inhibit the inflammatory response and improve peak aerobic exercise capacity in patients with recently decompensated systolic HF.
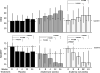
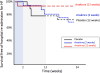
Methods and results: We randomly assigned 60 patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (<50%) and elevated C-reactive protein levels (>2 mg/L), within 14 days of hospital discharge, to daily subcutaneous injections with anakinra 100 mg for 2 weeks, 12 weeks, or placebo. Patients underwent measurement of peak oxygen consumption (Vo2 [mL/kg per minute]) and ventilatory efficiency (the VE/Vco2 slope). Treatment with anakinra did not affect peak Vo2 or VE/Vco2 slope at 2 weeks. At 12 weeks, patients continued on anakinra showed an improvement in peak Vo2 from 14.5 (10.5-16.6) mL/kg per minute to 16.1 (13.2-18.6) mL/kg per minute (P=0.009 for within-group changes), whereas no significant changes occurred within the anakinra 2-week or placebo groups. The between-groups differences, however, were not statistically significant. The incidence of death or rehospitalization for HF at 24 weeks was 6%, 31%, and 30%, in the anakinra 12-week, anakinra 2-week, and placebo groups, respectively (log-rank test P=0.10).
Conclusions: No change in peak Vo2 occurred at 2 weeks in patients with recently decompensated systolic HF treated with anakinra, whereas an improvement was seen in those patients in whom anakinra was continued for 12 weeks. Additional larger studies are needed to validate the effects of prolonged anakinra on peak Vo2 and rehospitalization for HF.
Clinical trial registration: URL: http://www.clinicaltrials.gov. Unique identifier: NCT01936909.
Keywords: heart failure; heart failure, systolic; inflammation; interleukin-1; myocardial infarction.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Keenan PS, Normand SLT, Lin Z, Drye EE, Bhat KR, Ross JS, Schuur JD, Stauffer BD, Bernheim SM, Epstein AJ, Wang Y, Herrin J, Chen J, Federer JJ, Mattera JA, Wang Y, Krumholz HM. An administrative claims measure suitable for profiling hospital performance on the basis of 30-day all-cause readmission rates among patients with heart failure. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2008;1:29–37. - PubMed
-
- Heidenreich PA, Albert NM, Allen LA, Bluemke DA, Butler J, Fonarow GC, Ikonomidis JS, Khavjou O, Konstam MA, Maddox TM, Nichol G, Pham M, Pina IL, Trogdon JG. Forecasting the impact of heart failure in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circ Heart Fail. 2014;6:606–619. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Van Tassell BW, Raleigh JMV, Abbate A. Targeting Interleukin-1 in Heart Failure and Inflammatory Heart Disease. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2015;12:33–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

