Human stem cell-derived astrocytes replicate human prions in a PRNP genotype-dependent manner
- PMID: 29141869
- PMCID: PMC5716027
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20161547
Human stem cell-derived astrocytes replicate human prions in a PRNP genotype-dependent manner
Abstract
Prions are infectious agents that cause neurodegenerative diseases such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD). The absence of a human cell culture model that replicates human prions has hampered prion disease research for decades. In this paper, we show that astrocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) support the replication of prions from brain samples of CJD patients. For experimental exposure of astrocytes to variant CJD (vCJD), the kinetics of prion replication occur in a prion protein codon 129 genotype-dependent manner, reflecting the genotype-dependent susceptibility to clinical vCJD found in patients. Furthermore, iPSC-derived astrocytes can replicate prions associated with the major sporadic CJD strains found in human patients. Lastly, we demonstrate the subpassage of prions from infected to naive astrocyte cultures, indicating the generation of prion infectivity in vitro. Our study addresses a long-standing gap in the repertoire of human prion disease research, providing a new in vitro system for accelerated mechanistic studies and drug discovery.
© 2017 Krejciova et al.
Figures
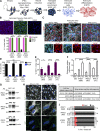
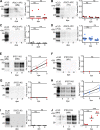

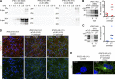
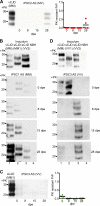
Comment in
-
A role for astroglia in prion diseases.J Exp Med. 2017 Dec 4;214(12):3477-3479. doi: 10.1084/jem.20172045. Epub 2017 Nov 21. J Exp Med. 2017. PMID: 29162644 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asuni A.A., Gray B., Bailey J., Skipp P., Perry V.H., and O’Connor V.. 2014. Analysis of the hippocampal proteome in ME7 prion disease reveals a predominant astrocytic signature and highlights the brain-restricted production of clusterin in chronic neurodegeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 289:4532–4545. 10.1074/jbc.M113.502690 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bishop M.T., Hart P., Aitchison L., Baybutt H.N., Plinston C., Thomson V., Tuzi N.L., Head M.W., Ironside J.W., Will R.G., and Manson J.C.. 2006. Predicting susceptibility and incubation time of human-to-human transmission of vCJD. Lancet Neurol. 5:393–398. 10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70413-6 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/D/20251967/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900580/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 MH099595/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/N013255/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600953/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P30 EY002162/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- BBS/E/D/20251968/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- NC/N001419/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

