Role of MicroRNA Regulation in Obesity-Associated Breast Cancer: Nutritional Perspectives
- PMID: 29141971
- PMCID: PMC5682994
- DOI: 10.3945/an.117.015800
Role of MicroRNA Regulation in Obesity-Associated Breast Cancer: Nutritional Perspectives
Abstract
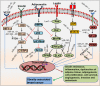
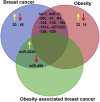
Breast cancer is the most common malignancy diagnosed in women, and the incidence of breast cancer is increasing every year. Obesity has been identified as one of the major risk factors for breast cancer progression. The mechanisms by which obesity contributes to breast cancer development is not yet understood; however, there are a few mechanisms counted as potential producers of breast cancer in obesity, including insulin resistance, chronic inflammation and inflammatory cytokines, adipokines, and sex hormones. Recent emerging evidence suggests that alterations in microRNA (miRNA) expressions are found in several diseases, including breast cancer and obesity; however, miRNA roles in obesity-linked breast cancer are beginning to unravel. miRNAs are thought to be potential noninvasive biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of cancer patients with comorbid conditions of obesity as well as therapeutic targets. Recent studies have evidenced that nutrients and other dietary factors protect against cancer and obesity through modulation of miRNA expressions. Herein, we summarize a comprehensive overview of up-to-date information related to miRNAs and their molecular targets involved in obesity-associated breast cancer. We also address the mechanisms by which dietary factors modulate miRNA expression and its protective roles in obesity-associated breast cancer. It is hoped that this review would provide new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of obesity-associated breast cancer to reduce the burden of breast cancer.
Keywords: adipocyte; breast cancer; dietary components; microRNA; obesity.
© 2017 American Society for Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: RK and DR, no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures. Boston (MA): American Cancer Society; 2016.
-
- Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y, Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Altieri A, Cogliano V; WHO International Agency for Research on Cancer Monograph Working Group. Carcinogenicity of alcoholic beverages. Lancet Oncol 2007;8:292–3. - PubMed
-
- Key J, Hodgson S, Omar RZ, Jensen TK, Thompson SG, Boobis AR, Davies DS, Elliott P. Meta-analysis of studies of alcohol and breast cancer with consideration of the methodological issues. Cancer Causes Control 2006;17:759–70. - PubMed
-
- Economopoulou P, Dimitriadis G, Psyrri A. Beyond BRCA: new hereditary breast cancer susceptibility genes. Cancer Treat Rev 2015;41:1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

