Candida auris: a Review of the Literature
- PMID: 29142078
- PMCID: PMC5740969
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00029-17
Candida auris: a Review of the Literature
Abstract
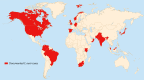
The emerging pathogen Candida auris has been associated with nosocomial outbreaks on five continents. Genetic analysis indicates the simultaneous emergence of separate clades of this organism in different geographical locations. Invasive infection and colonization have been detected predominantly in patients in high-dependency settings and have garnered attention due to variable antifungal resistance profiles and transmission within units instituting a range of infection prevention and control measures. Issues with the identification of C. auris using both phenotypic and molecular techniques have raised concerns about detecting the true scale of the problem. This review considers the literature available on C. auris and highlights the key unknowns, which will provide direction for further work in this field.
Keywords: Candida auris; emerging infection; nosocomial transmission.
© Crown copyright 2017.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical