A comprehensive structural, biochemical and biological profiling of the human NUDIX hydrolase family
- PMID: 29142246
- PMCID: PMC5688067
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-01642-w
A comprehensive structural, biochemical and biological profiling of the human NUDIX hydrolase family
Abstract
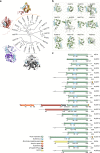
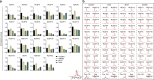
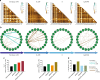
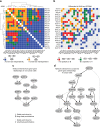
The NUDIX enzymes are involved in cellular metabolism and homeostasis, as well as mRNA processing. Although highly conserved throughout all organisms, their biological roles and biochemical redundancies remain largely unclear. To address this, we globally resolve their individual properties and inter-relationships. We purify 18 of the human NUDIX proteins and screen 52 substrates, providing a substrate redundancy map. Using crystal structures, we generate sequence alignment analyses revealing four major structural classes. To a certain extent, their substrate preference redundancies correlate with structural classes, thus linking structure and activity relationships. To elucidate interdependence among the NUDIX hydrolases, we pairwise deplete them generating an epistatic interaction map, evaluate cell cycle perturbations upon knockdown in normal and cancer cells, and analyse their protein and mRNA expression in normal and cancer tissues. Using a novel FUSION algorithm, we integrate all data creating a comprehensive NUDIX enzyme profile map, which will prove fundamental to understanding their biological functionality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- McLennan AG. The MutT motif family of nucleotide phosphohydrolases in man and human pathogens (review) Int. J. Mol. Med. 1999;4:79–89. - PubMed
-
- Sakumi K, et al. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human enzyme that hydrolyzes 8-oxo-dGTP, a mutagenic substrate for DNA synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:23524–23530. - PubMed

