Extract of Bauhinia vahlii Shows Antihyperglycemic Activity, Reverses Oxidative Stress, and Protects against Liver Damage in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 29142421
- PMCID: PMC5669104
- DOI: 10.4103/pm.pm_4_17
Extract of Bauhinia vahlii Shows Antihyperglycemic Activity, Reverses Oxidative Stress, and Protects against Liver Damage in Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
Background: Several studies have affirmed the effectiveness of some Bauhinia plants as antihyperglycemic agents.
Objective: We investigated the possible effect of Bauhinia vahlii leaves extract in reducing hyperglycemia and reversing signs of organ damage associated with diabetes in streptozotocin (STZ) rat model.
Materials and methods: Both polar fraction of the B. vahlii leaves (defatted ethanolic extract [DEE]) and nonpolar fraction (n-hexane extract) were evaluated in vitro for α-glucosidase inhibition and 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical scavenging potential. DEE was selected for further in vivo studies and was administered at two doses, i.e., 150 or 300 mg/kg to STZ-diabetic rats for 4 weeks.
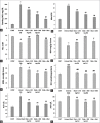
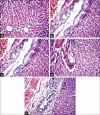
Results: Only DEE exhibited in vitro antioxidant and antihyperglycemic activities and its oral administration at both dose levels resulted in significant reduction in fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin. Furthermore, signs of oxidative stress as indicated by hepatic reduced glutathione, nitric oxide, and malondialdehyde levels were completely reversed. In addition, histopathological examination and measurement of serum aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase levels showed that DEE protected the liver from signs of liver pathogenesis when compared to diabetic untreated animals and those treated with metformin. Phytochemical analysis of DEE showed high flavonoids content with quercitrin as the major constituent along with other quercetin glycosides.
Conclusion: This study strongly highlights the possible beneficial effect of B. vahlii leaves extract in relieving hyperglycemia and liver damage in STZ-diabetic rats and recommends further investigation of the value of quercetin derivatives in controlling diabetes and ameliorating liver damage associated with it.
Summary: The polar fraction of the Bauhinia vahlii leaves (defatted ethanolic extract [DEE]) exhibited both in vitro antioxidant activity in 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl scavenging assay and strong α-glucosidase inhibition while the nonpolar fraction (n-hexane extract) failed to show any activity in both assays. DEE was further investigated in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat model where oral administration of DEE at 2 doses (150 and 300 mg/kg) for 4 weeks resulted in significant reduction in fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin and reversal of oxidative stress signs as indicated by measurement of hepatic reduced glutathione, nitric oxide, and malondialdehyde levels. In addition, histopathological examination and measurement of serum aspartate transaminase and alanine transaminase levels showed that DEE protected the liver from signs of pathogenesis observed in diabetic untreated rats. Phytochemical analysis of DEE showed high flavonoid content with quercitrin as the major constituent (62.9 ± 0.18 mg/mg). Abbreviations used: ALT: Alanine transaminase, AST: Aspartate transaminase, DEE: Defatted ethanol extract, DPPH: 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl, FBG: Fasting blood glucose, GAE: Gallic acid equivalent, GSH: Reduced glutathione, Hb1Ac: Glycated hemoglobin, HE: Hexane extract MDA: Malondialdehyde, QE: Quercetin equivalent, STZ: Streptozotocin, TAC: Total antioxidant capacity.
Keywords: Antihyperglycemic; Bauhinia vahlii; antioxidant; quercitrin; α-glucosidase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methanol-Extract/Fractions of Dacryodes edulis Leaves Ameliorate Hyperglycemia and Associated Oxidative Stress in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats.J Evid Based Integr Med. 2019 Jan-Dec;24:2515690X19843832. doi: 10.1177/2515690X19843832. J Evid Based Integr Med. 2019. PMID: 31055945 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of liver function, antioxidant responses, insulin resistance and glucose transport by Oroxylum indicum stem bark in STZ induced diabetic rats.Food Chem Toxicol. 2013 Dec;62:722-31. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2013.09.035. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 24140466
-
Hepatoprotective action of various partitions of methanol extract of Bauhinia purpurea leaves against paracetamol-induced liver toxicity: involvement of the antioxidant mechanisms.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016 Jun 11;16:175. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1110-4. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2016. PMID: 27287196 Free PMC article.
-
Launaea acanthodes (Boiss) O. Kuntze mediates hepatic glucose metabolism and ameliorates impaired pancreatic function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Mar 25;268:113577. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113577. Epub 2020 Nov 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33171271
-
Hepatoprotective and hypoglycemic effects of a tannin rich extract from Ximenia americana var. caffra root.Phytomedicine. 2017 Sep 15;33:36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 3. Phytomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28887918
Cited by
-
Chemical and biological investigations of Limonium axillare reveal mechanistic evidence for its antidiabetic activity.PLoS One. 2021 Aug 6;16(8):e0255904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0255904. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34358274 Free PMC article.
-
Trigonella foenum-graecum L. and Psoralea corylifolia L. Improve Erectile Dysfunction in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats through Suppression of Oxidative Stress.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 6;2022:4187359. doi: 10.1155/2022/4187359. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35707467 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baynes JW, Thorpe SR. Role of oxidative stress in diabetic complications: A new perspective on an old paradigm. Diabetes. 1999;48:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Cechinel Filho V. Chemical composition and biological potential of plants from the genus Bauhinia. Phytother Res. 2009;23:1347–54. - PubMed
-
- Mali RG, Mahajan SG, Mehta AA. Rakta kanchan (Bauhinia variegata): Chemistry, traditional and medicinal uses – A review. Pharmacogn Rev. 2007;1:314–6.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
