Characterization of the Phenolic Compound, Gallic Acid from Sansevieria roxburghiana Schult and Schult. f. Rhizomes and Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities Evaluation
- PMID: 29142435
- PMCID: PMC5669118
- DOI: 10.4103/pm.pm_497_16
Characterization of the Phenolic Compound, Gallic Acid from Sansevieria roxburghiana Schult and Schult. f. Rhizomes and Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities Evaluation
Abstract
Background: Sansevieria roxburghiana Schult. and Schult. f. (Asparagaceae) grows in India, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, and tropical Africa. Even though the plant has been traditionally used for the treatment of many ailments, the antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of S. roxburghiana methanol extract and its fractions have not yet been explored.
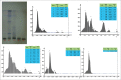
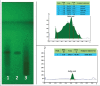
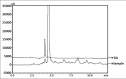
Materials and methods: Quantitative estimation of phenols and different antioxidant assays were performed using standard methods. Anti-proliferative effect of the extract and fractions were evaluated in HCT-116, HeLa, MCF-7, HepG2, and A-549 cancer cell lines by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) and sulforhodamine B (SRB) assay methods. High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) fingerprint profiling were carried out for extract and different fractions.
Results: Significant antioxidant and anti-proliferate activity were detected in ethyl acetate fraction. Ethyl acetate fraction showed prominent scavenging activity in 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt, and nitric oxide antioxidant assays with an concentration yielding 50% inhibition (IC50) 15.33 ± 1.45, 45.3 ± 1.93 and 48.43 ± 0.46 mg/ml, respectively. Cytotoxicity of ethyl acetate fraction was the highest among other fractions against HCT-116, HeLa, and MCF-7cancer cell lines with IC50 values 16.55 ± 1.28, 12.38 ± 1.36, and 8.03 ± 1.9 μg/ml, respectively, by MTT assay and 15.57 ± 0.70, 13.19 ± 0.49, and 10.34 ± 0.9 μg/ml, respectively, by SRB assay. The presence of gallic acid in the ethyl acetate fraction of S. roxburghiana rhizomes was confirmed by HPLC and HPTLC analysis.
Conclusion: Results suggested that ethyl acetate fraction exhibited effective antioxidant and antiproliferative activities. The phenolic compounds identified in ethyl acetate fraction could be responsible for the activities.
Summary: Sansevieria roxburghiana has been selected for in vitro antioxidant and cytotoxicity screeningEthyl acetate fraction of methanol extract of S. roxburghiana exhibited effective antioxidant and antiproliferative activitiesThe activity of ethyl acetate fraction may be due to the presence of phenolic compound which is identified by high-performance liquid chromatography and high-performance thin layer chromatography techniques. Abbreviations used: %: Percent, ºC: Celsius, mg: Microgram, ml-Microlitre, ANOVA: Analysis of variance, DMSO: Dimethyl sulfoxide, g: Grams, IC50: Concentration yielding 50% inhibition, Kg: Kilogram, mg: Milligram, min: Minutes, ml: Milliliter, HPLC: High-performance liquid chromatography, HPTLC: High-performance thin layer chromatography, DPPH: 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, ABTS: 2,2'-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) diammonium salt, MTT: 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide, GAE: Gallic acid equivalents, SRME: Methanol extract of S. roxburghiana, ROS: Reactive oxygen species, SRPE: Petroleum ether fraction of S. roxburghiana, SREA: Ethyl acetate fraction of S. roxburghiana, SRAQ: Aqueous fraction of S. roxburghiana, DMEM: Dulbecco's Minimum Essential Medium, FBS: Fetal bovine serum, OD: Optical density, TPC: Total phenolic content, SRBU: Butanol fraction of S. roxburghiana.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Sansevieria roxburghiana; antiproliferative; high-performance liquid chromatography; high-performance thin layer chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and Nephroprotective Activities of the Extract and Fractions of Homonoia riparia Lour.Pharmacogn Mag. 2017 Jan-Mar;13(49):25-30. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.197647. Pharmacogn Mag. 2017. PMID: 28216879 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids Derived from Abelmoschus esculentus Attenuates UV-B Induced Cell Damage in Human Dermal Fibroblasts Through Nrf2-ARE Pathway.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 May;12(Suppl 2):S129-38. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.182175. Epub 2016 May 11. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27279697 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical screening, phenolic and flavonoid contents, antioxidant and cytogenotoxicity activities of Combretum leprosum Mart. (Combretaceae).J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2021 May 19;84(10):399-417. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2021.1875345. Epub 2021 Jan 25. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2021. PMID: 33494643
-
Separation Methods of Phenolic Compounds from Plant Extract as Antioxidant Agents Candidate.Plants (Basel). 2024 Mar 27;13(7):965. doi: 10.3390/plants13070965. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assay of glucocerebrosidases using high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescent substrates.2021 Oct 6 [updated 2022 May 11]. In: Nishihara S, Angata K, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Hirabayashi J, editors. Glycoscience Protocols (GlycoPODv2) [Internet]. Saitama (JP): Japan Consortium for Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; 2021–. 2021 Oct 6 [updated 2022 May 11]. In: Nishihara S, Angata K, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Hirabayashi J, editors. Glycoscience Protocols (GlycoPODv2) [Internet]. Saitama (JP): Japan Consortium for Glycobiology and Glycotechnology; 2021–. PMID: 37590631 Free Books & Documents. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Prakash O, Kumar A, Kumar P Ajeet. Anticancer potential of plants and natural products: A Review. Am J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;1:104–15.
-
- Alan NH. The Use of Herbs and Natural Plant Compounds in the Fight Against Cancer. Cancer support association, Information, Wellness and Healing. [Last accessed 2016 Jul 21]. Available from: http://www.canceractive.com/cancer-active-page-link.aspx?n=1415 .
-
- Jimuty R, Mohammed K, Bilkis B, Choudhury H. Evaluation of analgesic, cytotoxic and antioxidant activities of Sansevieria roxburghiana Schult. and Schult. f. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012;2(2):S723–5.
-
- Haldar PK, Kar B, Bala A, Bhattacharya S, Mazumder UK. Antitumor activity of Sansevieria roxburghiana rhizome against Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mice. Pharm Biol. 2010;48:1337–43. - PubMed
-
- Hartwell JL. Plants Used Against Cancer. Massachusetts: Quaterman Pub; 1982. p. 340.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
