Dachaihu decoction ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting macrophage infiltration in chronic pancreatitis
- PMID: 29142471
- PMCID: PMC5677205
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7242
Dachaihu decoction ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting macrophage infiltration in chronic pancreatitis
Abstract
Aim: To explore the role of macrophages in chronic pancreatitis (CP) and the effect of Dachaihu decoction (DCHD) on pancreatic fibrosis in mice.
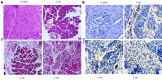
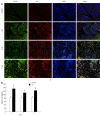
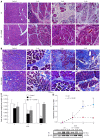
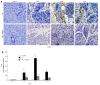
Methods: KunMing mice were randomly divided into a control group, CP group, and DCHD group. In the CP and DCHD groups, mice were intraperitoneally injected with 20% L-arginine (3 g/kg twice 1 d/wk for 6 wk). Mice in the DCHD group were administered DCHD intragastrically at a dose of 14 g/kg/d 1 wk after CP induction. At 2 wk, 4 wk and 6 wk post-modeling, the morphology of the pancreas was observed using hematoxylin and eosin, and Masson staining. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) serum levels were assayed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Double immunofluorescence staining was performed to observe the co-expression of F4/80 and IL-6 in the pancreas. Inflammatory factors including monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), macrophage inflammatory protein-1α (MIP-1α) and IL-6 were determined using real time-polymerase chain reaction. Western blot analysis was used to detect fibronectin levels in the pancreas.
Results: Compared with the control group, mice with 20% L-arginine-induced CP had obvious macrophage infiltration and a higher level of fibrosis. IL-6 serum concentrations were significantly increased. Double immunofluorescence staining showed that IL-6 and F4/80 were co-expressed in the pancreas. With the administration of DCHD, the infiltration of macrophages and degree of fibrosis in the pancreas were significantly attenuated; IL-6, MCP-1 and MIP-1α mRNA, and fibronectin levels were reduced.
Conclusion: The dominant role of macrophages in the development of CP was mainly related to IL-6 production. DCHD was effective in ameliorating pancreatic fibrosis by inhibiting macrophage infiltration and inflammatory factor secretion in the pancreas.
Keywords: Dachaihu decoction; Interleukin-6; Macrophages; Pancreatic fibrosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures
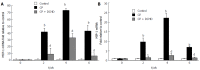
Similar articles
-
[Effect of DaChaiHu Decoction on pancreatic fibrosis induced by DBTC combined with alcohol and the mechanism of TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2016 May 8;32(5):444-448. doi: 10.13459/j.cnki.cjap.2016.05.015. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 29931849 Chinese.
-
Dachaihu Decoction alleviates chronic pancreatitis by regulating MAPK signaling pathway: Insights from network pharmacology and experimental validation.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 30;337(Pt 1):118833. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118833. Epub 2024 Sep 20. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39306212
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligands in Cigarette Smoke Induce Production of Interleukin-22 to Promote Pancreatic Fibrosis in Models of Chronic Pancreatitis.Gastroenterology. 2016 Dec;151(6):1206-1217. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.09.064. Epub 2016 Oct 18. Gastroenterology. 2016. PMID: 27769811 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of Chinese Herbal Medicines in the Treatment of Pancreatic Fibrosis.Am J Chin Med. 2019;47(4):709-726. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X1950037X. Epub 2019 May 15. Am J Chin Med. 2019. PMID: 31091974 Review.
-
[Progress on historical evolution, clinical application, and pharmacological effects of Dachaihu Decoction and predictive analysis of its quality markers].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024 Apr;49(8):2064-2075. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20231209.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38812223 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Da-Chai-Hu-Tang Protects From Acute Intrahepatic Cholestasis by Inhibiting Hepatic Inflammation and Bile Accumulation via Activation of PPARα.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 15;13:847483. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.847483. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35370715 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Changes and Pathological Pain Associated with Sedentary Lifestyle-Induced Body Systems Fat Accumulation and Their Modulation by Physical Exercise.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Dec 17;18(24):13333. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413333. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34948944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and therapeutic targeting of the CCL2/CCR2 signaling axis in inflammatory and fibrotic diseases.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 9;15:1497026. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1497026. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39850880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Botanical drugs and their natural compounds: a neglected treasury for inhibiting the carcinogenesis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):853-873. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2421759. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 39520705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography and Laboratory Parameters as Non-Invasive Diagnostic Markers of Pancreatic Fibrosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 21;13(14):2435. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13142435. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37510179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Muniraj T, Aslanian HR, Farrell J, Jamidar PA. Chronic pancreatitis, a comprehensive review and update. Part I: epidemiology, etiology, risk factors, genetics, pathophysiology, and clinical features. Dis Mon. 2014;60:530–550. - PubMed
-
- Madro A, Slomka M, Celinski K. Can we expect progress in the treatment of fibrosis in the course of chronic pancreatitis? Adv Med Sci. 2011;56:132–137. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

