Clinical and pathological characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas in Portugal
- PMID: 29142476
- PMCID: PMC5677199
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i40.7292
Clinical and pathological characterization of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas in Portugal
Abstract
Aim: To determine the prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated gastric carcinomas in the North Region of Portugal and to study its clinicopathological characteristics.
Methods: We have performed a retrospective study including a total of 179 consecutive patients with gastric cancer (GC) submitted to gastrectomy during 2011 at the Portuguese Oncology Institute of Porto. Clinical and pathological data was collected from individual clinical records and inserted on a database with unique codification. Tumour tissues were collected from the institutional tumour bank. EBV was detected by in situ hybridization for the detection of EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) and EBV latent proteins (LMP1 and LMP2A) were detected by immunohistochemistry.
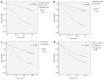
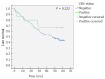
Results: The analysis showed that EBV-associated gastric carcinomas (EBVaGC) represents 8.4% (15/179) of all GC cases, with a significant differential distribution among histological types (P < 0.001): 100% (3/3) of medullary carcinomas, 100% (1/1) of adenosquamous carcinoma, 8.7% (8/92) of tubular adenocarcinomas, 8.0% (2/25) of mixed carcinomas and 2% (1/51) in poorly cohesive carcinomas. The analysis revealed a higher predominance of EBVaGC in the upper third and middle (cardia, fundus and body) of the stomach (P = 0.041), a significant lower number of regional lymph nodes invasion (P = 0.025) and a tendency for better prognosis (P = 0.222). EBV latent protein expression revealed that all EBVaGC cases were LMP1-negative, nevertheless 6 cases (40%) expressed LPM2A, which reveals that these cases show a distinct EBV-Latency profile (latency II-like).
Conclusion: EBVaGC represents 8.4% of all GC in the North Region of Portugal. The EBV-infected patients have specific clinic-pathological features that should be further explored to develop new strategies of management and treatment.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus; Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas; Gastric cancer; Prevalencel.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests in the reported study.
Figures

References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin D, Forman D, Bray F. GLOBOCAN 2012 v1.0, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No. 11 [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available from: http://globocan.iarc.fr/
-
- Ferlay J, Steliarova-Foucher E, Lortet-Tieulent J, Rosso S, Coebergh JW, Comber H, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49:1374–1403. - PubMed
-
- Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:757–768. - PubMed
-
- Lee JH, Kim SH, Han SH, An JS, Lee ES, Kim YS. Clinicopathological and molecular characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:354–365. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

