In vitro and in vivo comparative and competitive activity-based protein profiling of GH29 α-l-fucosidases
- PMID: 29142681
- PMCID: PMC5654414
- DOI: 10.1039/c4sc03739a
In vitro and in vivo comparative and competitive activity-based protein profiling of GH29 α-l-fucosidases
Abstract
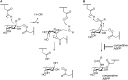
GH29 α-l-fucosidases catalyze the hydrolysis of α-l-fucosidic linkages. Deficiency in human lysosomal α-l-fucosidase (FUCA1) leads to the recessively inherited disorder, fucosidosis. Herein we describe the development of fucopyranose-configured cyclophellitol aziridines as activity-based probes (ABPs) for selective in vitro and in vivo labeling of GH29 α-l-fucosidases from bacteria, mice and man. Crystallographic analysis on bacterial α-l-fucosidase confirms that the ABPs act by covalent modification of the active site nucleophile. Competitive activity-based protein profiling identified l-fuconojirimycin as the single GH29 α-l-fucosidase inhibitor from eight configurational isomers.
Figures








References
-
- Intra J., Perotti M.-E., Pavesi G., Horner D. Gene. 2007;392:34–46. - PubMed
-
- Liu S. W., Chen C. S., Chang S. S., Mong K. K. T., Lin C. H., Chang C. W., Tang C. Y., Li Y. K. Biochemistry. 2009;48:110–120. - PubMed
-
- Guillotin L., Lafite P., Daniellou R. Biochemistry. 2014;53:1447–1455. - PubMed
-
- Cobucci-Ponzano B., Mazzone M., Rossi M., Moracci M. Biochemistry. 2005;44:6331–6342. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

