Classification of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease based on convolutional neural network and reinforcement sample learning algorithm
- PMID: 29142739
- PMCID: PMC5662529
- DOI: 10.1007/s13755-017-0029-6
Classification of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis disease based on convolutional neural network and reinforcement sample learning algorithm
Abstract
Electromyogram (EMG) signals contain useful information of the neuromuscular diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ALS is a well-known brain disease, which can progressively degenerate the motor neurons. In this paper, we propose a deep learning based method for efficient classification of ALS and normal EMG signals. Spectrogram, continuous wavelet transform (CWT), and smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution (SPWVD) have been employed for time-frequency (T-F) representation of EMG signals. A convolutional neural network is employed to classify these features. In it, Two convolution layers, two pooling layer, a fully connected layer and a lost function layer is considered in CNN architecture. The CNN architecture is trained with the reinforcement sample learning strategy. The efficiency of the proposed implementation is tested on publicly available EMG dataset. The dataset contains 89 ALS and 133 normal EMG signals with 24 kHz sampling frequency. Experimental results show 96.80% accuracy. The obtained results are also compared with other methods, which show the superiority of the proposed method.
Keywords: Convolutional neural networks; Electromyogram (EMG) signals; Reinforcement sample learning and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); Time–frequency representation.
Figures
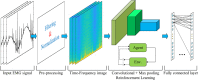
References
-
- Merletti R, Farina D. Surface electromyography: physiology, engineering and applications. Wiley-IEEE Press. 2016. ISBN: 978-1-119-08287-3.
-
- Fattah SA, Doulah ABMSU, Iqbal MA, Shahnaz C, et al. Identification of motor neuron disease using wavelet domain features extracted from EMG signal. In: 2013 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and System, pp. 1308–1311.
-
- Gokgoz E, Subasi A. Comparison of decision tree algorithms for EMG signal classification using DWT. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2015;18:138–144. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2014.12.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

