Combined empirical mode decomposition and texture features for skin lesion classification using quadratic support vector machine
- PMID: 29142740
- PMCID: PMC5662531
- DOI: 10.1007/s13755-017-0033-x
Combined empirical mode decomposition and texture features for skin lesion classification using quadratic support vector machine
Abstract
Purpose: Basal cell carcinoma is one of the most common malignant skin lesions. Automated lesion identification and classification using image processing techniques is highly required to reduce the diagnosis errors.
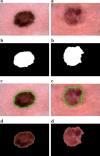
Methods: In this study, a novel technique is applied to classify skin lesion images into two classes, namely the malignant Basal cell carcinoma and the benign nevus. A hybrid combination of bi-dimensional empirical mode decomposition and gray-level difference method features is proposed after hair removal. The combined features are further classified using quadratic support vector machine (Q-SVM).
Results: The proposed system has achieved outstanding performance of 100% accuracy, sensitivity and specificity compared to other support vector machine procedures as well as with different extracted features.
Conclusion: Basal Cell Carcinoma is effectively classified using Q-SVM with the proposed combined features.
Keywords: Basal cell carcinoma; Empirical mode decomposition; Gray-level difference method; Riesz; Skin cancer classification; Support vector machine.
Figures








Similar articles
-
A novel cumulative level difference mean based GLDM and modified ABCD features ranked using eigenvector centrality approach for four skin lesion types classification.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Oct;165:163-174. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.08.009. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30337071
-
Integration of morphological preprocessing and fractal based feature extraction with recursive feature elimination for skin lesion types classification.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019 Sep;178:201-218. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.06.018. Epub 2019 Jun 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2019. PMID: 31416550
-
Differentiation of fat-poor angiomyolipoma from clear cell renal cell carcinoma in contrast-enhanced MDCT images using quantitative feature classification.Med Phys. 2017 Jul;44(7):3604-3614. doi: 10.1002/mp.12258. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28376281
-
Computer-assisted lip diagnosis on Traditional Chinese Medicine using multi-class support vector machines.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012 Aug 16;12:127. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-12-127. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 22898352 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning Approaches Towards Skin Lesion Segmentation and Classification from Dermoscopic Images - A Review.Curr Med Imaging. 2020;16(5):513-533. doi: 10.2174/1573405615666190129120449. Curr Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32484086 Review.
Cited by
-
Guest editorial: special issue on "Artificial Intelligence in Health and Medicine".Health Inf Sci Syst. 2018 Jan 16;6(1):2. doi: 10.1007/s13755-017-0040-y. eCollection 2018 Dec. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2018. PMID: 29354261 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Automated detection of nonmelanoma skin cancer using digital images: a systematic review.BMC Med Imaging. 2019 Feb 28;19(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s12880-019-0307-7. BMC Med Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30819133 Free PMC article.
-
Skin lesion classification using multi-resolution empirical mode decomposition and local binary pattern.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 20;17(9):e0274896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274896. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36126072 Free PMC article.
-
The accuracy of artificial intelligence used for non-melanoma skin cancer diagnoses: a meta-analysis.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023 Jul 28;23(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s12911-023-02229-w. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2023. PMID: 37501114 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Diepgen TL, Mahler V. The epidemiology of skin cancer. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146(Suppl 61):2262–2269. - PubMed
-
- Yuan, X, Yang Z, Zouridakis G, Mullani N. SVM-based texture classification and application to early melanoma detection. In: 28th annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, 2006 (EMBS’06), pp. 4775–4778. IEEE, New York; 2006. - PubMed
-
- Lau HT, Al-Jumaily A. Automatically early detection of skin cancer: study based on neural network classification. In: International conference of IEEE soft computing and pattern recognition, 2009 (SOCPAR’09) (2009).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

