[Foramen magnum meningiomas: A report of 12 cases and literature review]
- PMID: 29142778
- PMCID: PMC5672662
- DOI: 10.4103/sni.sni_277_17
[Foramen magnum meningiomas: A report of 12 cases and literature review]
Abstract
Objectives: The primary aim of this study was to assess the results attained for 12 patients with an anterior or lateral foramen magnum meningioma, treated microsurgically.
Methods: Between June 2005 and December 2016, 12 patients with foramen magnum meningiomas underwent microsurgical resection. Patients' age and gender, tumor localization (anterior or lateral), symptoms, approach, and postoperative results were analyzed.
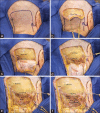
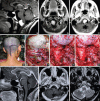
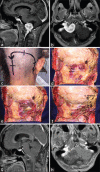
Results: Eight of the 12 patients were women. The average age of the patients was 47 years. In 8 patients, the tumor was located anteriorly and in 4 patients laterally. The main symptom was occipitocervical pain (8 patients), followed by tetraparesia (3 patients). For all the anterior foramen magnum meningiomas, an extreme-lateral transcondylar approach was performed. In cases where the tumor was lateral, an extreme-lateral retrocondylar approach was adopted. Total and subtotal resection was achieved in 10 and 2 patients, respectively. In the latter instances, a very small piece of tumor remained around the vertebral artery or inside the jugular foramen. Three patients exhibited postoperative cranial nerve XII palsy and 2 cranial nerve XI palsy. One patient experienced cerebrospinal fluid leakage.
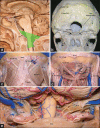
Conclusions: Microsurgery for both anterior and lateral foramen magnum meningiomas can be performed safely and effectively. What is necessary is: (a) good anatomical knowledge of the region; (b) two-step muscle dissection to expose the suboccipital triangle and vertebral artery; (c) to adopt an extreme-lateral retrocondylar approach for lateral meningiomas, and an extreme-lateral transcondylar approach for anterior tumors; and (d) good microsurgical techniques.
Objetivo:: El propósito del presente trabajo es presentar los resultados de 12 pacientes con diagnóstico de meningiomas del foramen magno (MFM), de localización anterior o lateral, operados con técnicas microquirúrgicas.
Método:: Desde Junio de 2005 a Diciembre de 2016, 12 pacientes con diagnóstico de MFM fueron intervenidos quirúrgicamente. Se evaluó: edad, sexo, localización de la lesión (anterior o lateral), sintomatología, tipo de abordaje utilizado y resultados postoperatorios.
Resultados:: De los pacientes intervenidos, 8 fueron mujeres y 4 varones. La edad promedio fue de 47 años. La localización fue anterior en 8 casos y lateral en 4 casos. La sintomatología más frecuente fue dolor occipito-cervical (8 casos), seguido de tetraparesia (3 casos). En los pacientes con MFM de localización anterior se realizó un abordaje extremo-lateral transcondilar (ELTC), mientras que en los tumores laterales el abordaje fue extremo-lateral retrocondilar (ELRC). En 10 casos la resección fue completa. En dos pacientes fue necesario dejar una pequeña lámina de meningioma sobre la arteria vertebral y a nivel del foramen yugular. Como complicaciones postoperatorias, 3 pacientes presentaron una paresia del XII nervio craneano y 2 pacientes paresia del XI nervio craneano; además, 1 paciente presentó una fístula de LCR.
Conclusión:: La cirugía de los MFM de localización anterior y lateral puede ser realizada de forma segura y efectiva. Es necesario: a) buen conocimiento anatómico de la región; b) disecar los músculos de la nuca en 2 planos, exponiendo el triángulo suboccipital y la arteria vertebral (AV); 3) realizar un abordaje ELRC en los tumores laterales, y ELTC en los tumores anteriores; y 4) buena técnica microquirúrgica.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Surgery on anterior foramen magnum meningiomas using a conventional posterior suboccipital approach: a report on an experience with 17 cases.Neurosurgery. 2001 Jul;49(1):102-6; discussion 106-7. doi: 10.1097/00006123-200107000-00016. Neurosurgery. 2001. PMID: 11440430 Review.
-
Vertebral Artery Transposition Via an Extreme-Lateral Approach for Anterior Foramen Magnum Meningioma or Craniocervical Junction Tumors.World Neurosurg. 2016 Apr;88:154-165. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2015.12.073. Epub 2015 Dec 31. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26748172
-
Foramen Magnum Meningioma: Microsurgical Endoscopic-Controlled Resection via a Lateral Suboccipital Retrocondylar Approach with Preservation of Posterior Arch of Atlas Integrity.J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2019 Dec;80(Suppl 4):S352-S354. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1698822. Epub 2019 Oct 22. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base. 2019. PMID: 31750059 Free PMC article.
-
Lateral suboccipital retrosigmoid retrocondylar approach for foramen magnum meningiomas.J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2018 Jul-Sep;9(3):175-181. doi: 10.4103/jcvjs.JCVJS_38_18. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2018. PMID: 30443137 Free PMC article.
-
Foramen Magnum Meningiomas: A Report of 10 Cases and Literature Review.Turk Neurosurg. 2021;31(6):931-935. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.33015-20.2. Turk Neurosurg. 2021. PMID: 35018625 Review.
Cited by
-
Classification and microsurgical treatment of foramen magnum meningioma.Chin Neurosurg J. 2023 Jan 24;9(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s41016-022-00315-y. Chin Neurosurg J. 2023. PMID: 36691052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acikbas SC, Tuncer R, Demirez I, Rahat O, Kazan S, Sindel M, et al. The effect of condylectomy on extreme lateral transcondylar approach to the anterior foramen magnum. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 1997;139:546–50. - PubMed
-
- Arnautovic KI, Al-Mefty O, Husain M. Ventral foramen magnum meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2000;92(Suppl 1):71–80. - PubMed
-
- Babu RP, Sekhar LN, Wright DC. Extreme lateral transcondylar approach: Technical improvements and lessons learned. J Neurosurg. 1994;81:49–59. - PubMed
-
- Bassiouni H, Ntoukas V, Asgari S, Sandalcioglu EI, Stolke D, Seifert V. Foramen magnum meningiomas: Clinical outcome after microsurgical resection via a posterolateral suboccipital retrocondylar approach. Neurosurgery. 2006;59:1177–87. - PubMed
-
- Bertalanffy H, Seeger W. The dorsolateral, suboccipital, transcondylar approach to the lower clivus and anterior portion of the craniocervical junction. Neurosurgery. 1991;29:815–21. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
