Analytical study of effective biodegradation of p-cresol using Serratia marcescens ABHI001: application in bioremediation
- PMID: 29142804
- PMCID: PMC5662518
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-017-1006-0
Analytical study of effective biodegradation of p-cresol using Serratia marcescens ABHI001: application in bioremediation
Abstract
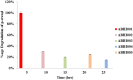
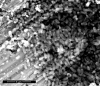
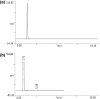
This study evaluated the capability of Serratia marcescens ABHI001 to effectively degrade p-cresol through different techniques. The molecular identity of the laboratory isolate S. marcescens ABHI001 was confirmed through the 16S ribosomal DNA gene pattern, and its morphological features were investigated through field-emission scanning electron microscopy. In addition, the degradation behavior of the isolate for cresol was verified using several techniques, including UV-visible spectroscopy, followed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography, and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The maximum degradation percentage of 85% for p-cresol could be achieved after 18 h of incubation with S. marcescens ABHI001. The formation of p-hydroxybenzaldehyde, p-hydroxybenzoate, and protocatechuate metabolites was confirmed through HPLC. The study results indicate that S. marcescens ABHI001 may have applications in the bioremediation of organic pollutants, such as p-cresol.
Keywords: Biodegradation; Organic pollutants; Serratia marcescens; p-Cresol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Figures




References
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) Toxicological profile for cresols (Draft) Altanta: US Public Health Service, US Department of Health & Human Services; 1990.
-
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) Toxicological profile for cresols. Altanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service; 2008. - PubMed
-
- Al-Khalid T, El-Naas MH. Aerobic biodegradation of phenols: a comprehensive review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol. 2012;42:1631–1690. doi: 10.1080/10643389.2011.569872. - DOI
-
- Ansari AA, Gill SS, Gill R, Lanza GR, Newman L. Phytoremediation: Management of environmental contaminants. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing AG; 2016.
-
- Balarak D, Mahdavi Y. Survey of efficiency agricultural waste as adsorbent for removal of p-Cresol from aqueous solution. Int Res J Pure Appl Chem. 2016;10:1–11. doi: 10.9734/IRJPAC/2016/20507. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

