Sustained release of stem cell factor in a double network hydrogel for ex vivo culture of cord blood-derived CD34+ cells
- PMID: 29143396
- PMCID: PMC6528907
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12407
Sustained release of stem cell factor in a double network hydrogel for ex vivo culture of cord blood-derived CD34+ cells
Abstract
Objectives: Stem cell factor (SCF) is considered as a commonly indispensable cytokine for proliferation of haematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), which is used in large dosages during ex vivo culture. The work presented here aimed to reduce the consumption of SCF by sustained release but still support cells proliferation and maintain the multipotency of HSCs.
Materials and methods: Stem cell factor was physically encapsulated within a hyaluronic acid/gelatin double network (HGDN) hydrogel to achieve a slow release rate. CD34+ cells were cultured within the SCF-loaded HGDN hydrogel for 14 days. The cell number, phenotype and functional capacity were investigated after culture.
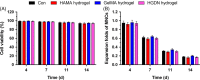
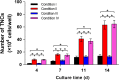
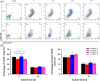
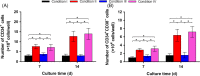
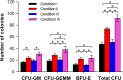
Results: The HGDN hydrogels had desirable properties and encapsulated SCF kept being released for more than 6 days. SCF remained the native bioactivity, and the proliferation of HSCs within the SCF-loaded HGDN hydrogel was not affected, although the consumption of SCF was only a quarter in comparison with the conventional culture. Moreover, CD34+ cells harvested from the SCF-loaded HGDN hydrogels generated more multipotent colony-forming units (CFU-GEMM).
Conclusion: The data suggested that the SCF-loaded HGDN hydrogel could support ex vivo culture of HSCs, thus providing a cost-effective culture protocol for HSCs.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Survival of cord blood haematopoietic stem cells in a hyaluronan hydrogel for ex vivo biomimicry.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013 Nov;7(11):901-10. doi: 10.1002/term.1482. Epub 2012 Mar 31. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013. PMID: 22473677
-
The use of covalently immobilized stem cell factor to selectively affect hematopoietic stem cell activity within a gelatin hydrogel.Biomaterials. 2015 Oct;67:297-307. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.07.042. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 26232879 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization of SCF feeding regimen for ex vivo expansion of cord blood hematopoietic stem cells.J Biotechnol. 2012 Dec 15;164(2):211-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2012.08.007. Epub 2012 Aug 29. J Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22954892
-
Ex vivo expansion of CD34+ umbilical cord blood cells in a defined serum-free medium (QBSF-60) with early effect cytokines.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 1999 Dec;8(6):609-18. doi: 10.1089/152581699319777. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 1999. PMID: 10645768
-
Stem cell factor is essential for preserving NOD/SCID reconstitution capacity of ex vivo expanded cord blood CD34(+) cells.Cell Prolif. 2015 Jun;48(3):293-300. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12186. Epub 2015 Apr 21. Cell Prolif. 2015. PMID: 25899394 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
miR-9-5p Suppresses Malignant Biological Behaviors of Human Gastric Cancer Cells by Negative Regulation of TNFAIP8L3.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Oct;64(10):2823-2829. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05626-2. Epub 2019 May 28. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31140050
-
Recent advances in engineering hydrogels for niche biomimicking and hematopoietic stem cell culturing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 24;10:1049965. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1049965. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36507253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimulation of C-Kit+ Retinal Progenitor Cells by Stem Cell Factor Confers Protection Against Retinal Degeneration.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Mar 31;13:796380. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.796380. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35431956 Free PMC article.
-
An Injectable silk-based hydrogel as a novel biomineralization seedbed for critical-sized bone defect regeneration.Bioact Mater. 2024 Feb 8;35:274-290. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.01.024. eCollection 2024 May. Bioact Mater. 2024. PMID: 38370865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chua K‐N, Chai C, Lee P‐C, et al. Surface‐aminated electrospun nanofibers enhance adhesion and expansion of human umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Biomaterials. 2006;27:6043‐6051. - PubMed
-
- Thomas ED, Blume KG. Historical markers in the development of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 1999;5:341‐346. - PubMed
-
- Cohen Y, Nagler A. Umbilical cord blood transplantation–how, when and for whom? Blood Rev. 2004;18:167‐179. - PubMed
-
- Raic A, Rodling L, Kalbacher H, Lee‐Thedieck C. Biomimetic macroporous PEG hydrogels as 3D scaffolds for the multiplication of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Biomaterials. 2014;35:929‐940. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

