Physical activity in the prevention of human diseases: role of epigenetic modifications
- PMID: 29143608
- PMCID: PMC5688489
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-4193-5
Physical activity in the prevention of human diseases: role of epigenetic modifications
Abstract
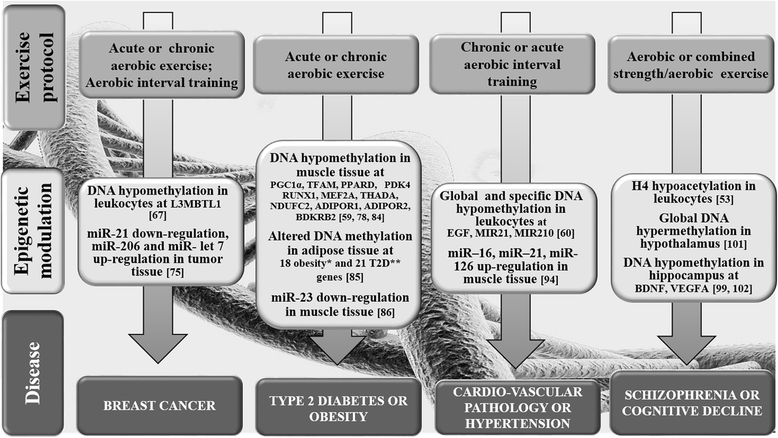
Epigenetic modification refers to heritable changes in gene function that cannot be explained by alterations in the DNA sequence. The current literature clearly demonstrates that the epigenetic response is highly dynamic and influenced by different biological and environmental factors such as aging, nutrient availability and physical exercise. As such, it is well accepted that physical activity and exercise can modulate gene expression through epigenetic alternations although the type and duration of exercise eliciting specific epigenetic effects that can result in health benefits and prevent chronic diseases remains to be determined. This review highlights the most significant findings from epigenetic studies involving physical activity/exercise interventions known to benefit chronic diseases such as metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: DNA methylation; Disease prevention; Exercise; Histone modification.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that there are not conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Russo VEA, Martienssen RA, Riggs AD: Epigenetic mechanisms of gene regulation. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor Press 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

