Skullcap (Scutellaria Baicalensis) Hexane Fraction Inhibits the Permeation of Ovalbumin and Regulates Th1/2 Immune Responses
- PMID: 29143798
- PMCID: PMC5707656
- DOI: 10.3390/nu9111184
Skullcap (Scutellaria Baicalensis) Hexane Fraction Inhibits the Permeation of Ovalbumin and Regulates Th1/2 Immune Responses
Abstract
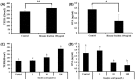
Skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) is well known for its anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. In our previous study, we found that skullcap could inhibit allergen permeation and regulate Th1/2 immune balance. To reveal the key fractions and components of skullcap, we fractionated skullcap extract into five fractions: hexane, chloroform, ethyl acetate, butanol, and water fraction. Among these fractions, the hexane fraction significantly suppressed the production of Th2-mediated cytokines (Interleukin (IL)-4, 5, 10 and 13) and increased Th1-mediated cytokines (Interferon (IFN)-γ and IL-12). Furthermore, the hexane fraction inhibited the permeation of ovalbumin (OVA), used as an allergen, across the intestinal epithelial cell monolayer. To confirm the active compounds in the hexane fraction, fatty acids were analyzed. Linoleic acid (LA, C18:2 (>59.7%)) was identified as the most important fatty acid in the skullcap hexane fraction. LA significantly suppressed IL-4 production and increased IFN-γ secretion, as well as inhibiting OVA permeation. Thus, LA significantly diminished the permeation of allergen by enhancing intestinal barrier function and regulated allergic responses to maintain Th1/Th2 immune balance.
Keywords: Scutellaria baicalensis; Th1/2 immune response; Th1/Th2 balance; linoleic acid; ovalbumin permeation; skullcap.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory effect of skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) extract on ovalbumin permeation in vitro and in vivo.Food Chem. 2013 Sep 1;140(1-2):22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.042. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23578610
-
Skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) extract and its active compound, wogonin, inhibit ovalbumin-induced Th2-mediated response.Molecules. 2014 Feb 21;19(2):2536-45. doi: 10.3390/molecules19022536. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 24566319 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive effects of skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) extract in a mouse model of food allergy.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 May 14;153(3):667-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.018. Epub 2014 Mar 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24637193
-
The role of nebulized IFN-gamma in the modulation of allergic responses.Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996;409:17-23. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-5855-2_3. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1996. PMID: 9095219 Review. No abstract available.
-
The Use of Chinese Skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis) and Its Extracts for Sustainable Animal Production.Animals (Basel). 2021 Apr 7;11(4):1039. doi: 10.3390/ani11041039. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targets and Potential Mechanism of Scutellaria baicalensis in Treatment of Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on Bioinformatics Analysis.J Oncol. 2022 Feb 12;2022:8762717. doi: 10.1155/2022/8762717. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35190740 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Medicinal Plants Conferring Protection Against Ovalbumin-Induced Asthma in Experimental Animals: A Review.J Asthma Allergy. 2021 Jun 14;14:641-662. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S296391. eCollection 2021. J Asthma Allergy. 2021. PMID: 34163178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small phenolic and indolic gut-dependent molecules in the primate central nervous system: levels vs. bioactivity.Metabolomics. 2022 Jan 6;18(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s11306-021-01866-4. Metabolomics. 2022. PMID: 34989922
-
Anti-inflammatory diets reduce the risk of excessive gestational weight gain in urban South Africans from the Soweto First 1000-Day Study (S1000).Eur J Nutr. 2022 Dec;61(8):3929-3941. doi: 10.1007/s00394-022-02931-x. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Eur J Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35764725 Free PMC article.
-
Lamiaceae: An Insight on Their Anti-Allergic Potential and Its Mechanisms of Action.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jun 19;10:677. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00677. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31275149 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gao J., Sanchez-Medina A., Pendry B.A., Hughes M.J., Webb G.P., Corcoran O. Validation of a HPLC method for flavonoid biomarkers in sckullcap (Scutellaria) and its use to illustrate wide variability in the quality of commercial tinctures. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008;11:77–87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

