Epstein-Barr Virus Hijacks DNA Damage Response Transducers to Orchestrate Its Life Cycle
- PMID: 29144413
- PMCID: PMC5707548
- DOI: 10.3390/v9110341
Epstein-Barr Virus Hijacks DNA Damage Response Transducers to Orchestrate Its Life Cycle
Abstract
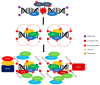
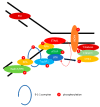
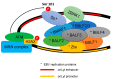
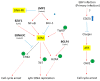
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous virus that infects most of the human population. EBV infection is associated with multiple human cancers, including Burkitt's lymphoma, Hodgkin's lymphoma, a subset of gastric carcinomas, and almost all undifferentiated non-keratinizing nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Intensive research has shown that EBV triggers a DNA damage response (DDR) during primary infection and lytic reactivation. The EBV-encoded viral proteins have been implicated in deregulating the DDR signaling pathways. The consequences of DDR inactivation lead to genomic instability and promote cellular transformation. This review summarizes the current understanding of the relationship between EBV infection and the DDR transducers, including ATM (ataxia telangiectasia mutated), ATR (ATM and Rad3-related), and DNA-PK (DNA-dependent protein kinase), and discusses how EBV manipulates the DDR signaling pathways to complete the replication process of viral DNA during lytic reactivation.
Keywords: DNA damage response; Epstein–Barr virus; lytic reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR-18a reactivates the Epstein-Barr virus through defective DNA damage response and promotes genomic instability in EBV-associated lymphomas.BMC Cancer. 2018 Dec 29;18(1):1293. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-5205-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30594162 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Damage Signaling Is Induced in the Absence of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Lytic DNA Replication and in Response to Expression of ZEBRA.PLoS One. 2015 May 7;10(5):e0126088. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126088. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25950714 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-γ-inducible protein 16 (IFI16) is required for the maintenance of Epstein-Barr virus latency.Virol J. 2017 Nov 13;14(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0891-5. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 29132393 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Related Lymphoproliferative Disorders in Ataxia Telangiectasia: Does ATM Regulate EBV Life Cycle?Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 4;9:3060. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03060. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30662441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the latent-lytic switch in Epstein-Barr virus.Semin Cancer Biol. 2014 Jun;26:60-8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.01.002. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014. PMID: 24457012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus and human herpesvirus 8 salivary shedding in HIV positive men who have sex with men with controlled and uncontrolled plasma HIV viremia: a 24-month longitudinal study.BMC Infect Dis. 2018 Dec 19;18(1):683. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3591-x. BMC Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30567494 Free PMC article.
-
p62-mediated Selective autophagy endows virus-transformed cells with insusceptibility to DNA damage under oxidative stress.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Apr 24;15(4):e1007541. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007541. eCollection 2019 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31017975 Free PMC article.
-
In-Depth Analysis of Genetic Variation Associated with Severe West Nile Viral Disease.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Dec 8;8(4):744. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8040744. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33302579 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus replication within differentiated epithelia requires pRb sequestration of activator E2F transcription factors.J Virol. 2024 Oct 22;98(10):e0099524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00995-24. Epub 2024 Sep 18. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39291960 Free PMC article.
-
ATR activated by EB virus facilitates chemotherapy resistance to cisplatin or 5-fluorouracil in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Jan 9;11:573-585. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S187099. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 30666155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Epstein A. Why and how epstein-barr virus was discovered 50 years ago. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015;390:3–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

