Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease
- PMID: 29144438
- PMCID: PMC5745501
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox6040091
Bioactive Components in Moringa Oleifera Leaves Protect against Chronic Disease
Abstract
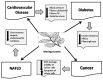
Moringa Oleifera (MO), a plant from the family Moringacea is a major crop in Asia and Africa. MO has been studied for its health properties, attributed to the numerous bioactive components, including vitamins, phenolic acids, flavonoids, isothiocyanates, tannins and saponins, which are present in significant amounts in various components of the plant. Moringa Oleifera leaves are the most widely studied and they have shown to be beneficial in several chronic conditions, including hypercholesterolemia, high blood pressure, diabetes, insulin resistance, non-alcoholic liver disease, cancer and overall inflammation. In this review, we present information on the beneficial results that have been reported on the prevention and alleviation of these chronic conditions in various animal models and in cell studies. The existing limited information on human studies and Moringa Oleifera leaves is also presented. Overall, it has been well documented that Moringa Oleifera leaves are a good strategic for various conditions associated with heart disease, diabetes, cancer and fatty liver.
Keywords: Moringa Oleifera; bioactive components; cancer; diabetes; heart disease; hepatic steatosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Padayachee B., Baijnath H. An overview of the medicinal importance of Moringaceae. J. Med. Plants Res. 2012;6:5831–5839.
-
- Martin C., Martin G., Garcia A., Fernández T., Hernández E., Puls L. Potential applications of Moringa oleifera. A critical review. Pastosy Forrajes. 2013;36:150–158.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

