Structure and assembly of the Ebola virus nucleocapsid
- PMID: 29144446
- PMCID: PMC5714281
- DOI: 10.1038/nature24490
Structure and assembly of the Ebola virus nucleocapsid
Abstract
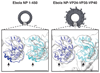
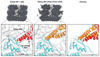
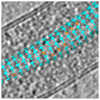
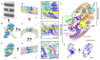
Ebola and Marburg viruses are filoviruses: filamentous, enveloped viruses that cause haemorrhagic fever. Filoviruses are within the order Mononegavirales, which also includes rabies virus, measles virus, and respiratory syncytial virus. Mononegaviruses have non-segmented, single-stranded negative-sense RNA genomes that are encapsidated by nucleoprotein and other viral proteins to form a helical nucleocapsid. The nucleocapsid acts as a scaffold for virus assembly and as a template for genome transcription and replication. Insights into nucleoprotein-nucleoprotein interactions have been derived from structural studies of oligomerized, RNA-encapsidating nucleoprotein, and cryo-electron microscopy of nucleocapsid or nucleocapsid-like structures. There have been no high-resolution reconstructions of complete mononegavirus nucleocapsids. Here we apply cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the structure of Ebola virus nucleocapsid within intact viruses and recombinant nucleocapsid-like assemblies. These structures reveal the identity and arrangement of the nucleocapsid components, and suggest that the formation of an extended α-helix from the disordered carboxy-terminal region of nucleoprotein-core links nucleoprotein oligomerization, nucleocapsid condensation, RNA encapsidation, and accessory protein recruitment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
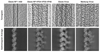
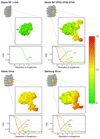
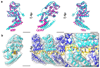


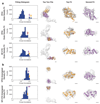
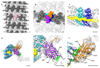
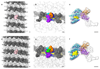
References
-
- Feldmann H, Sanchez A, Geisbert T. In: Fields virology. Knipe David M, Howley Peter M., editors. Lippincott Williams Wilkins; 2013. pp. 923–956.
-
- Lamb RA. In: Fields Virology. Knipe David M, Howley Peter M., editors. Vol. 30. Lippincott Williams Wilkins; 2013. pp. 880–884.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

