Zika virus: An updated review of competent or naturally infected mosquitoes
- PMID: 29145400
- PMCID: PMC5690600
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005933
Zika virus: An updated review of competent or naturally infected mosquitoes
Abstract
Zika virus (ZIKV) is an arthropod-borne virus (arbovirus) that recently caused outbreaks in the Americas. Over the past 60 years, this virus has been observed circulating among African, Asian, and Pacific Island populations, but little attention has been paid by the scientific community until the discovery that large-scale urban ZIKV outbreaks were associated with neurological complications such as microcephaly and several other neurological malformations in fetuses and newborns. This paper is a systematic review intended to list all mosquito species studied for ZIKV infection or for their vector competence. We discuss whether studies on ZIKV vectors have brought enough evidence to formally exclude other mosquitoes than Aedes species (and particularly Aedes aegypti) to be ZIKV vectors. From 1952 to August 15, 2017, ZIKV has been studied in 53 mosquito species, including 6 Anopheles, 26 Aedes, 11 Culex, 2 Lutzia, 3 Coquillettidia, 2 Mansonia, 2 Eretmapodites, and 1 Uranotaenia. Among those, ZIKV was isolated from 16 different Aedes species. The only species other than Aedes genus for which ZIKV was isolated were Anopheles coustani, Anopheles gambiae, Culex perfuscus, and Mansonia uniformis. Vector competence assays were performed on 22 different mosquito species, including 13 Aedes, 7 Culex, and 2 Anopheles species with, as a result, the discovery that A. aegypti and Aedes albopictus were competent for ZIKV, as well as some other Aedes species, and that there was a controversy surrounding Culex quinquefasciatus competence. Although Culex, Anopheles, and most of Aedes species were generally observed to be refractory to ZIKV infection, other potential vectors transmitting ZIKV should be explored.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
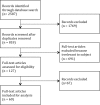
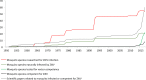
References
-
- Dick GWA, Kitchen SF, Haddow AJ. Zika Virus (I). Isolations and serological specificity. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1952;46: 509–520. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(52)90042-4 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hayes EB. Zika Virus Outside Africa. Emerg Infect Dis. 2009;15: 1347–1350. doi: 10.3201/eid1509.090442 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Haddow AD, Schuh AJ, Yasuda CY, Kasper MR, Heang V, Huy R, et al. Genetic characterization of Zika virus strains: geographic expansion of the Asian lineage. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6: e1477 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001477 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duffy MR, Chen T- H, Hancock WT, Powers AM, Kool JL, Lanciotti RS, et al. Zika virus outbreak on Yap Island, Federated States of Micronesia. N Engl J Med. 2009;360: 2536–2543. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805715 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cao-Lormeau V-M, Roche C, Teissier A, Robin E, Berry A-L, Mallet H-P, et al. Zika Virus, French Polynesia, South Pacific, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2014;20: 1085–1086. doi: 10.3201/eid2006.140138 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

